* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Notes Unit 4 Part 8
Epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
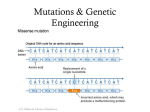
BIOLOGY NOTES GENETICS PART 8 PAGES 252-285 NAME: DAY / MOD: DATE: Standards: ____ Explain how mutations in DNA sequences may or may not result in phenotypic change. Explain how mutations in gametes may result in phenotypic changes of offspring. ____ Evaluate the impact of biotechnology on the individual, society, and the environment, including medical and ethical issues ____ Describe how mutation and genetic recombination increase genetic variation Essential Questions: 1. 2. 3. I. Mutations Mutation = a change in an organism’s ________ mutations are ____________ and can have unpredictable effects errors in DNA provide the ______________ that is fundamental to the evolution of a species most mutations result in ___________ or the lack of normal development in an organism if the mutation occurs in ____________, birth defects can occur if the mutation occurs in ____________, cancer may occur mutagens = factors in the _______________ that cause mutations to occur e.g. carcinogen = mutagens that specifically cause _________ e.g. Types of Mutations: A. Gene Mutation = mutations that involve a change in the sequence of _______________ within a ___________ gene occur most often during ______ replication so affect _____________ cells more often phenotype may or may ______ be altered depending on type of mutation Types of Gene Mutations: 1. point mutation = a gene mutation involving changes in ____ or few nucleotides usually only ______ amino acid is effected a. substitution - a mutation in which one base is ______________ for another 2. frameshift mutation = a gene mutation in which the “reading _________” of the genetic message is _____________ changes the __________ amino acid sequence drastically changes the __________ so that it is unable to perform its normal _____________ a. insertion - a nucleotide is ____________ to the genetic code b. deletion - a nucleotide is ____________ from the genetic code B. Chromosomal Mutation = mutations involved in changing the ____________ or ___________ of chromosomes chromosomal mutations occur in all organisms but most often in __________ Range, A. Unit 4 Page 2H usually occur because parts of ____________ are broken off or lost during _____________ when homologous chromosomes pair together so affect ____________ cells more often phenotype almost always _________________ since mutation involves a large number of ________ being affected non-disjunction = the failure of ____________ chromosomes to separate properly during meiosis e.g. Types of Chromosomal Mutations: a. Insertion – part of a _____________ breaks off and attaches to its sister chromatid DIAGRAM: b. Deletion – part of a _____________ is left out DIAGRAM: c. Inversion – part of a _________________ breaks out and is reinserted backwards DIAGRAM: d. Translocation – part of one _____________ breaks off and is added to a different chromosome DIAGRAM: II. Manipulating DNA & Biotechnology A. Cutting DNA Scientists can extract ______ from cells, cut it into small pieces, and individually study each piece Restriction enzymes = enzymes that cut ______ at a specific sequence of ________________ using restrictive enzymes allows scientists to read much __________ pieces of DNA at a time restriction enzymes are used by _______________ to defend against _____________ e.g. B. Organizing DNA Gel Electrophoresis = using electric ____________ applied to a gel mixture of ____ fragments in order to separate the DNA fragments based on their molecular ________ can be used to compare genomes of different organisms by using restriction _________ genome = an organism’s complete set of ______ within a cell can also be used to compare the gene sequences of organisms of the same species when used with _________ or a polymerase chain reaction, gel electrophoresis can be used as a type of DNA ______________ in crime labs to identify suspects. This is much more precise than simple ________ testing because the DNA of every __________ is different III. Genetic Engineering = making changes in the _____ code of living organisms Scientists today can use their knowledge of genetics in order to study and __________ the DNA within living organisms. Genetic engineering is useful because the genetic code is ______________!!! Range, A. Unit 4 Page 2H A. How Can DNA Be Changed? Cloning = creating a genetically identical copy of a _______ or of an organism first successfully cloned mammal was a sheep named _________ in 1997 does not necessarily mean the outcome will be _________________ due to environmental influences that could affect _________ expression useful in cloning organs for ____________ or possibly saving an endangered ____________ Recombinant DNA = DNA produced by combining the ________ from many different ____________ Genes responsible for producing specific _______________ can be extracted from an organism using ____________________ enzymes These genes can then be spliced into a plasmid plasmid = a small circular piece of _______ found naturally in some bacteria B. How Can Changed DNA (Recombinant DNA) Be Used? Once the foreign DNA is _________________ into the plasmid, the plasmid is returned to the bacteria transgenic = referring to organisms that contain __________ from a different organism within its genome If the plasmid is accepted, the foreign DNA will be replicated very fast as the bacteria multiply having lots of specific genes allows for those gene’s products to be _________________ as well transformed = referring to organisms containing foreign ______ that express the products of the new ___________ e.g. Sometimes the treated bacteria can be used to introduce the recombinant plasmid into ____________ cells or ______________ cells often, these plants and animals are referred to as GM or __________________ _________________ e.g. Since the genetic code is ___________________, recombinant DNA can also be used to cross genes among different ___________________ e.g. STUDENT SYNTHESIS To demonstrate knowledge of the information contained within these notes, within the space below EITHER 1. Create two higher level test questions and answers based on the information OR 2. Write a comprehensive summary of the information Range, A. Unit 4 Page 2H