* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mutations & Genetic Engineering
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified organism containment and escape wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified food wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
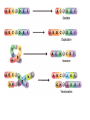
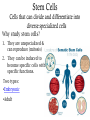
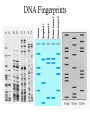
Mutations & Genetic Engineering Mutation A change in the nucleotide sequence of the genome of an organism Substitution A mutation that changes one base • Possible outcomes: – New codon codes for the same amino acid – silent – New codon changes the amino acid – missense • Sickle cell anemia – New codon codes for a stop codon – non sense Frameshift Mutations • A change in the reading pattern of the DNA • Causes: – Deletions • Sections of DNA are missing • Example: Williams Syndrome – Insertions • Mutations in which an extra base is inserted Involves changes in the number or structure of chromosomes • Deletion- loss of all or part – Cystic Fibrous • Duplication – segment is repeated –Huntington’s disease • Inversion – orientation is in the reverse direction • Translocation – two non homologous chromosomes exchange segments Genetic Engineering Manipulating an organism’s genome using biotechnology Genetically Modified Organisms (GMO) Organisms who have been genetically altered using biotechnology These are also referred to as transgenic organisms Transgenic Organisms • Microorganisms – Insulin production – Clotting Factors • Plants (GMOs) – Insect resistant – Weather Resistant • Mammals – Medicine – Commerical Cloning Making an exact genetic copy of an organism Why clone? 1. Medical purposes • Animal models • Stem cells • Drug production 2. Reviving extinct or endangered organisms 3. Pet trade Stem Cells Cells that can divide and differentiate into diverse specialized cells Why study stem cells? 1. They are unspecialized & can reproduce (mitosis) 2. They can be induced to become specific cells with specific functions. Two types: •Embryonic •Adult DNA Fingerprinting A method of isolating and making images of a person’s unique DNA sequence Process: Gel Electrophoresis with help from restriction enzymes DNA Fingerprints