* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 1 Test Review Guide
Survey
Document related concepts
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
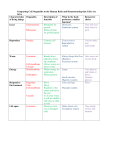
Name: __________________ Biology: CELLS UNIT REVIEW- 2014 This test will cover: Chapter 7 in textbook. The following questions provide an idea of the subject matter that will be covered and provide a beginning to your studying. Just because something is not on this sheet does not mean that it will not be on the test. Review all your notes, lab papers, vocabulary list and quizzes to prepare. 1. What type of cell is shown below? ___________________ List 3 things present in this cell that helps you determine the type of cell it is: 1._______________________ 2._______________________ 3._______________________ 2. Clearly and neatly DRAW an animal cell and add the following organelles: Nucleus, Nucleolus, Smooth ER, Rough ER, Golgi Body, Mitochondria, Ribosomes, Cell membrane, Centrioles (always a pair!), Lysosomes, Cytoplasm. Label each part! 3. What organelle is only found in animal cells? ________________ What is its function? __________________________________________ 4. What cell parts are found in ALL cells (both eukaryotic and prokaryotic) 1. _________________ 2. _________________ 3. _________________ 4. DNA 5. The three statements of cell theory: 1. All living things are made up of one or more ____________. 2. The cell is the smallest unit of ____________. 3. Cells come from existing ____________. Name the three scientists that are responsible for providing some of the first evidence for those ideas. _____________________, ____________________ & ___________________ 6. What organelle or cell part is described? Oval, produces ATP (energy), site of cellular respiration - __________________________ Oval, green, makes glucose, site of photosynthesis- _______________________________ Large, round, contains DNA, controls the cell, found in all eukaryotic cells- _____________ Smallest organelles, not membrane-bound, site of protein assembly from amino acids- _____ Largest organelle in plant cell, stores water and other substances- _________________ Network of tunnels that synthesize substances- _______________________ Found inside the nucleus, makes RNA (ribosomes are made of RNA) - _________________ Round, contains enzymes to break down substances within the cell- _________________ Semi-fluid substance containing chemicals for reactions taking place within the cell, the organelles “float” in this - ________________________ Boundary of the cell, regulates what enters and leaves the cell, made of phospholipids and proteins- ___________________ Rigid, outermost part of plant cell, contains cellulose- ____________________ Barrel shaped, always found in a pair, help with cell division- _____________________ 7. Diffusion is the movement of substances from an area of __________ concentration to an area of _________ _________________. Net flow of the substance will stop once an ___________________ is reached. A concentration ______________ is needed for diffusion to occur. 8. Osmosis is the movement of ________ from an area of __________ concentration to an area of _________ _________________. 9. In each diagram show the direction of net flow with an arrow ( see example): Assume the membrane is semi-permeable (selectively permeable) and will allow water, glucose and iodine to pass through but not starch or salt. example Semi permeable 10% iodine 2% iodine 10% NaCl Pure water 20% glucose 10% glucose 2% starch 10% starch A B C D 10. Which diagrams are showing the diffusion of a solute? _______________ 11. Which diagrams are showing osmosis? _____________________ 12. Label the parts of the prokaryotic cell: 13. Why do phospholipids orient themselves into a bilayer?__________________________ _ What part of the phospholipid is hydrophobic? ______________________ 5% glucose 10% glucose e E 14. Cell membranes are described by the ______________ mosaic model. This means the cell membrane is made up of many different pieces and that they can move around and change places! 15. Label the parts of the cell membrane and use the information on the diagram for questions below: 16. Proteins in the cell membrane can function as receptors or __________ to move substances from one side of the membrane to the other. This is known as _______________________ diffusion which is passive (does not require energy). If energy (ATP) is required to move a substance it is known as _____________ transport. 17. Simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion require NO energy and therefore are considered _______________________. Active transport does not require a concentration gradient; molecules can move against a gradient and therefore _______________ must be used. 18. Cells can move in (or out) molecules through the cell membrane. However, larger particles may require a different way of entering (or leaving) the cell. Define: Endocytosis- __________________________________________________________ Exocytosis- ___________________________________________________________ BE SURE TO THOROUGHLY COMPLETE THIS, STUDY IT and KNOW THIS INFORMATION FOR THE TEST. ALSO KNOW Structure and Function information from your table! Vocabulary list is posted on my webpage. However, we will cover the terms hypotonic, isotonic, hypertonic, plasmolysis and turgor pressure in January when we return from winter break!