* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Comparing Cell Organelles to the Human Body and
Survey
Document related concepts
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Somatic cell nuclear transfer wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Symbiogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
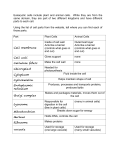
Comparing Cell Organelles to the Human Body and Demonstrating that Cells Are Alive Characteristics Organelles Description of What in the body Reason for of living things function performs a similar choice function? Chromosomes Blueprints for Hormones They tell your Grow growth Endocrine system body when to Ribosomes Makes protein grow for growth/repair Reproduce Nucleus Controls cell division Testes/ovaries Reproductive system Waste Lysosome Kidney/lungs/skin/liver Gets waste out (Bladder) of your body Excretory system Energy Cell membrane Vacuole Mitochondrion Breaks down particles, cleans up cytoplasm Allows waste out Stores waste Makes energy by respiration Photosynthesis Chloroplast Respond to Environment Flagellum Cilia Cell membrane Vacuole Life span Lysosome Move Move Regulates what enters and leaves the cell As it loses water, it will get smaller and cause a plant to wilt Destroys worn out or damaged cells Lungs Small intestine Digestive system Arms and legs Used to make new individuals Uses glucose and breaks it down Absorbs glucose Move Muscular system White blood cells Circulatory system They attack viruses and bacteria