* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology Chapter 3 Learning Objectives
Survey
Document related concepts
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
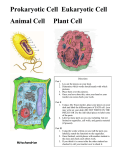
Biology Chapter 3 Learning Objectives Complete the following on a separate piece of paper. TRY TO COMPLETE WITHOUT THE HELP OF THE BOOK. Use the book to check your answers. 1. List the three parts of the Cell Theory. 2. Make a chart to contrast eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. Include what the name means, what is present or absent, and the types of organisms in each category. 3. Compare the size of a typical prokaryotic cell with that of a eukaryotic cell. 4. List the function and draw a picture of the following cell parts/organelles: cytoplasm, nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, golgi apparatus, mitochondria, vacuole, cell membrane, lysosomes, centriole, cell wall, chloroplasts. 5. Contrast animal cells and plant cells. Draw a diagram of each that highlights the parts where they differ. 6. List the organelles that are a part of the process of building, assembling, and transporting proteins, starting with ribosomes and ending with cell membrane. 7. Which cell parts are important in maintaining the cell’s shape & structure? 8. Which organelle is the site of cellular respiration? Which organelle is the site of photosynthesis? 9. Which organelle contains their own genetic information and ribosomes? 10. One organelle can be compared to a post office, which one is it and why is that analogy used? One organelle can be compared to a garbage disposal, which one is it and why is that analogy used? 11. Draw a labeled diagram of the cell membrane. Explain what a phosolipid is. 12. Describe the terms fluid mosaic model, lipid (phospholipid) bilayer, and selective permeability. 13. What is diffusion? How does concentration affect diffusion? 14. How is osmosis different from diffusion? 15. Contrast facilitative diffusion and active transport. What is involved with each type? 16. Draw a picture showing water movement in a cell placed in isotonic, hypertonic, and hypotonic solutions. Label where the salt concentration is highest. 17. Which type of solution can cause and animal cell to shrivel up? Which type of solution can cause and animal cell to burst? 18. Contrast endocytosis and exocytosis. Draw a picture of each. 19. Describe the main objective of the Eggsperiment Lab. What molecules moved across the membrane? 20. Explain the Elodea Lab. Include the terms osmosis, cell wall, cell membrane, and vacuole. 21. List 2 organelles and explain their relationship with 2 other organelles. 22. Describe the dialysis lab. Explain what molecules were and were not able to pass through the dialysis tubing and why. Review Problems (these are mandatory for full credit) P 95-96 #1-11, 14, 22, 23, 28, 30 and P 97 #1-6 This test will also include questions on scientific method (section 1.3) and the four main organic molecules (section 2.3). You may want to do the following optional review questions: p.31 #14-16 and p. 61 #16-18