* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download how do metal oxide varistors work
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
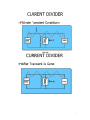
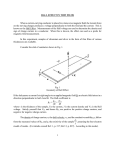
HOW DO METAL OXIDE VARISTORS WORK? Metal Oxide Varistor (MOV) technology is the most prevalent technology utilized in electrical transient protection products today. Many industry manufacturers, including Current Technology, integrate various sizes of radial or strap-type MOVs into their products: 20mm, 32mm and 40mm diameter MOVs are most commonly used. Does MOV size make a difference, and if so, what size delivers the best performance? What is an MOV? MOVs are non-linear bi-polar resistors which have a very high resistance (can be modeled as an open circuit) to the normal 60Hz sine wave (see Fig. 1A). Conduction begins when the voltage across an MOV reaches maximum continuous operating voltage (MCOV) - also known as "threshold voltage:" As the voltage increases, the MOV's resistance drops dramatically, eventually approaching zero (see Fig. 1B). Because of the low impedance at this higher voltage level, a properly designed transient suppression device will divert transient current through itself and away from sensitive loads. Since MOV-based devices are connected in parallel to the loads, the clamp voltage across the MOVs plus the voltage developed across the wiring and disconnect provided for the device is the maximum voltage that will appear across the load terminals. After the transient occurs, the MOV returns to normal stat, ready for the next transient (see Fig.1C). FIG 1A: FIG 1B: 1 FIG 1C: 2