* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biochemistry Test Review
Survey
Document related concepts
Enzyme inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
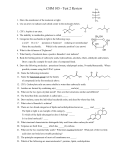
SBI 4UI Biochemistry Test Review Key terms: Functional group Alkane Alkene Alkyne Alcohol Carboxylic Acid Ketone Amine Amide Phosphate Ester Ether Aldehyde Carbohydrate Glucose Fructose Galactose Maltose Lactose Sucrose Starch Glycogen Chitin Lipids Glycerol Saturated Fatty Acid Unsaturated Fatty Acid Phospholipid Amphipathic Sterol Condensation Reaction Hydrolysis Reaction Amino Acid Polypeptide Primary protein structure Secondary protein structure Tertiary protein structure Quaternary protein structure Enzyme Lock and Key Theory Induced fit Theory Competitive inhibition Non-competitive inhibition Allosteric regulation Co-factor Co-enzyme Denature Nucleic Acid Nucleotide Purines Pyrimidines semi-permeable glycolipid glycoprotein globular protein cholesterol polar non-polar passive transport diffusion facilitated diffusion pinocytosis phagocytosis active transport In addition to knowing the key terms above, students should be able to know and do the following: 1. Name and draw simple alkane and allkene molecules of up to 10 carbons in length. 2. Name and draw simple alkanes of up to 10 carbons containing one of the following functional groups: alcohol, aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic acid, amine. 3. Recognize all of the following functional groups when present in an organic molecule: alcohol, aldehyde, amine, amide, carboxylic acid, ketone, ester, ether, phosphate. 4. Explain how functional groups allow organic molecules to be linked together. 5. Identify the sugars Glucose, Galactose and Fructose when the structure is given. 6. Be able to draw the ringed structure of glucose and show how two glucose units can join together to form maltose. Name the kind of reaction that links the sugars. 7. Identify key features of starch and glycogen. 8. Be able to draw a triglyceride, showing how glycerol and three fatty acids link together. Name the kind of reaction that links the fatty acids to glycerol. How many molecules of water are formed? 9. Distinguish between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids. 10. How do trans fats differ from other fats, both saturated and unsaturated? 11. Identify a phospholipid when the structure is given and be able to list the 5 components of a phospolipid. 12. Identify a sterol such as cholesterol when the structure is given and list some functions of cholesterol. 13. Be able to draw the basic structure of an amino acid and show how two or more amino acids may join together to form a polypeptide. Name the kind of reaction that links the amino acids. 14. Describe the four different levels of protein structure. 15. Define enzyme and give three examples of enzymes and the substrates they act upon. 16. Explain the difference between lock and key theory and induced fit theory. Which theory is now thought to be the most accurate picture of how enzymes bind to substrates? 17. Distinguish between competitive and non-competitive inhibition as they relate to enzyme action. 18. How can an enzyme’s action be slowed down or sped up by allosteric regulation? 19. List three conditions that can affect enzyme action. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. Name the two types of nucleic acids and list four important facts about each. Describe the parts of a nucleotide. Distinguish between purine and pyrimidine bases in general. Label the membrane diagram and state the function of the major membrane parts. Describe the permeability of the cell membrane. What types of molecules cross easily? What conditions seem to disrupt cell membranes most? (Hint: beet lab!) Distinguish between simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion. Distinguish between passive and active transport. Explain the Na+/K+ pump as an example of active transport. Textbook Questions: p. 31-33 #1, 2, 12, 14-17, 33 p. 59-61 #6-8, 10-14, 16-18, 20 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 7