* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download TFSD Unwrapped Standard 3rd Math Algebra sample
Survey
Document related concepts
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Dual inheritance theory wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
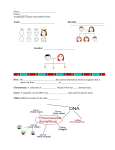
TFSD Unwrapped Standard Grade 10 - Biology Power Standard (s) Reference: Standard 7- Inheritance State Standard: Goal 1.2: Understand Concepts and Processes of Evidence, Models, and Explanation 9-10.B.1.2.1 Use observations and data as evidence on which to base scientific explanations. 9-10.B.1.2.2 Develop models to explain concepts or systems. 9-10.B.1.2.3 Develop scientific explanations based on knowledge, logic and analysis. Goal 1.4: Understand the Theory that Evolution is a Process that Relates to the Gradual Changes in the Universe and of Equilibrium as a Physical State Reference to 7.S.3.2.1 Goal 1.5: Understand Concepts of Form and Function Goal 1.8: Understand Technical Communication 9-10.B.1.8.1 Analyze technical writing, graphs, charts, and diagrams. Standard 3: Biology Students explain the importance of cells as they relate to the organization and structure of complex organisms, differentiation and specialization during development, and the chemical reactions necessary to sustain life. Students describe the functions of cell structures. Students use the theory of evolution to explain diversity of life. Goal 3.1: Understand the Theory of Biological Evolution 9-10.B.3.1.1 Use the theory of evolution to explain how species change over time. 9-10.B.3.1.2 Explain how evolution is the consequence of interactions among the potential of a species to increase its numbers, genetic variability, a finite supply of resources, and the selection by the environment of those offspring better able to survive and reproduce. Goal 3.3: Understand the Cell is the Basis of Form and Function for All Living Things 9-10.B.3.3.4 Explain how selective expression of genes can produce specialized cells from a single cell. Goal 5.2: Understand the Relationship between Science and Technology 9-10.B.5.2.1 Explain how science advances technology. 9-10.B.5.2.2 Explain how technology advances science. 9-10.B.5.2.3 Explain how science and technology are pursued for different purposes. National Standards A.1. Abilities necessary to do scientific inquiry C.1.f. Cells can differentiate, and complex multicellular organisms are formed as a highly organized arrangement of differentiated cells. C.2.a In all organisms, the instructions for specifying the characteristics of the organisms are carried in DNA. C.2.b. Most of the cells in a human contain two copies of each of 22 different chromosomes. In addition, there is a pair of chromosomes that determine sex. G.3. Historical Perspectives District Standard: TFSD Power Standard: Students will analyze how traits are related to genetics Concepts: Need to know about (Nouns) Gregor Mendel’s Peas Trait Gene Allele P (parental) generation F1 generation Mendel’s Laws of Heredity Punnett Squares Dominant allele: capital Recessive allele: lowercase phenotype: physical characteristics genotype: genetic makeup (tall plants only) homozygous: two identical alleles for a particular trait (tt or TT) heterozygous: two different alleles for the same trait Purebred Hybrid Independent Assortment Incomplete Dominance Codominance Multiple Alleles Polygenic Traits Phases of Meiosis Gamete Formation Comparing Mitosis and Meiosis Skills: Be able to do (Verb Phrases) Describe how Mendel studied inheritance in peas. Summarize Mendel’s conclusion about inheritance. Explain the principle of dominance. Describe what happens during segregation. Explain how geneticists use the principles of probability. Describe how geneticists use Punnett squares. Explain the principle of independent assortment. Explain how Mendel’s principles apply to organisms. Identifying Big Ideas from Unwrapped Standards: 1. The traits of an organism are dependent on its combination of dominant and recessive alleles. 2. Genetic mutations can be harmful and cause genetic disorders or they can be beneficial and offer advantages to organisms. 3. Sexual reproduction increases variation in offspring. 4. Parents contribute gametes that combine to form a zygote with a combination of traits from both parents. Essential Questions from Big Ideas to Guide Instruction and Assessment: 1. How are the characteristics of an organism determined? 2. How do mutations affect organisms? How does sexual reproduction affect variation? 3. How does sexual reproduction affect variation? 4. How are traits passed from parents to offspring? Possible Topics or Context: (what you will use to teach the concepts and skills-particular unit, lessons or activities) Pre-assessment o List some genetic traits that are found in your family. Allow students to discuss traits and why they believe traits differ among members of their family. Formative Assessment o o o o Punnett Squares: Given the genotypes of the parent generation, use a Punnett Square to predict the possible genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring. Analyze data from a Punnett Square to predict the mode of inheritance displayed by a trait. Genetics Lab (toothpick fish) Building Babies Lab Summative Assessment o You must write an article in a scientific journal about a genetic trait that you have discovered. Describe your research by explaining how meiosis allows the trait to be passed, the different combination of alleles for the trait, and a sample Punnett Square showing the mode of inheritance for the trait.