* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 6: Mendelian Genetics
Genetically modified organism containment and escape wikipedia , lookup
Dual inheritance theory wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
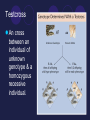
Mendelian Genetics Chapter 9 Gregor Mendel I love genetics!! 1843 - entered a monastery. 1851 – studied science & math at the University of Vienna Eventually returned to the monastery & used statistics to analyze the genetics of pea plants. Terminology Inheritance – The passing of traits by heredity. Heredity – The transmission of traits from parents to offspring. Pure – Always produce offspring with that trait. Strain – Describes all plants pure for a species. Pollination – Transfer of pollen from anther to stigma Mendel’s Experiments Grew pure plants Produced strains by allowing plants to selfpollinate. Crossed pollinated parental generation (P1) All offspring (F1) expressed the dominant trait. Self-pollinated the F1 plants & called offspring F2 generation. Mendel’s Experiments continued… Mendel’s Three Principles Genes: Chemical factors that determine traits Principle of Dominance & Recessiveness One factor in a pair may mask the other, preventing it from having an effect. Principle of Segregation Each reproductive cell receives one factor for a trait, therefore 2 factors separate during egg & sperm formation. Principle of Independent Assortment Factors for different characteristics are distributed to reproductive cells independently. Probability The likelihood that a specific event will occur. The principles of probability can be used to predict the outcomes of genetic crosses. General Terms Gene: segment of DNA on chromosomes that controls a particular hereditary trait. Allele: Each of several alternative forms of a gene. Represented by lower & upper case letters. Genotype: Genetic makeup of organism Phenotype: External appearance Homozygous: Both alleles of a pair are the same (ex. TT, tt) Heterozygous: Two alleles of a pair are not the same (ex. Tt) Genetic Crosses Monohybrid crosses: A cross between individuals that involves one pair of contrasting traits. Punnet Square: A diagram used to predict genetic probabilities. Genetic Crosses – Examples on the board Testcross An cross between an individual of unknown genotype & a homozygous recessive individual. Incomplete Dominance When two or more alleles influence the phenotype, resulting in an intermediate phenotype. R RR W R W WW RR:RW:WW Dihybrid Crosses A cross between individuals that involves two pairs of contrasting traits.