* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document 8885723
Survey
Document related concepts
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Bimolecular fluorescence complementation wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
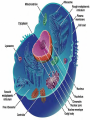
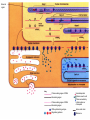
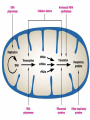
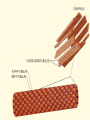
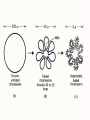
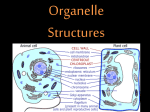
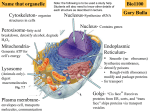
The nucleolus is a non-membrane bound structure composed of proteins and nucleic acids that is located within the nucleus. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is transcribed and assembled within the nucleolus. Nucleoli (plural for nucleolus) form around genetic loci termed Nucleolar Organizing Regions (NORs). NORs are composed of tandem repeats of rRNA genes found in several different chromosomes. Mitochondrion - 16,000 bp Chloroplast - 120,000 bp Eukaryote Nucleus - 3 billion bp Four types of genes Nuclear gene 1) Responds to regulatory signals - makes proteins for export. Nuclear gene 2) Responds to internal signals - makes proteins for use in cytoplasm. Nuclear gene 3) Makes proteins to be transported into an organelle. Organelle gene 4) Makes proteins for use inside its own organelle. Exported proteins are made on rough endoplasmic reticula (ER). Rough ER is smooth ER that is embedded with ribosomes. Cytosolic or organelle - destined proteins are made on free (unbound; not bound to ER) ribosomes. Proteins destined for organelles are tagged and are targeted to specific organelles. Only free ribosomes are found in organelles. External signal Protein-coding region of DNA Noncoding region Protein-coding region of RNA Noncoding region RNA-synthesizing enzyme Regulatory proteins Secreted protein Proteins used in cell Protein encoded by mitochondrion or chloroplast Amino acid chain Ribosome Centrosomes surrounded by starlike webs of protein filaments are the master architects of cell division. CENTRIOLES at the heart of the centrosomes in animal cells are tubelike structures. Each one is formed from nine rods; each rod consists of three microtubules fused along their length. A microtubule is a hollow fiber made of subunits that contain an alpha- and a beta-tubulin protein. The cytoplasmic microtubules organized by the centrosome seem to grow out of the pericentriolar material and not directly from the centrioles themselves. STRUCTURE OF CENTRIOLE Telomere – piece of DNA at the very tip of each cell’s chromosomes. Telomerase – enzyme that helps restore a portion of the telomere with each cell division. Dyskeratosis congenita – genetic disease causing accelerated shortening of telomeres. May result from lowered telomerase activity 1)Naked DNA 2)Nucleosome 3)Solenoid 4)Loop 5)Rosette 6)Coil 7)Chromatid Interphase Chromatin M-Phase