* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Rome
Survey
Document related concepts
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Demography of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Early Roman army wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Augustus wikipedia , lookup
Roman emperor wikipedia , lookup
History of the Constitution of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
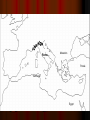
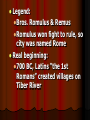
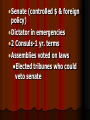
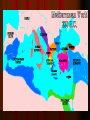
Rome Geography The Alps: mountains natural protection Mediterranean Sea: protection & trade Rome ROME Macedon Macedon Persia Persia Carthage Carthage Egypt Egypt Ancient Italy (c. 6th century B.C.) Etruscans (900-500 BC) Northern Italy Extravagant art Drained marshes, built sewers, paved roads Latins in central Italy (Rome) revolt against Etruscan king Etruscan pottery depicting Odysseus & his men fighting Cyclops Etruscan architectural plans (ca. 510 BC) Legend: Bros. Romulus & Remus Romulus won fight to rule, so city was named Rome Real beginning: 700 BC, Latins “the 1st Romans” created villages on Tiber River Roman Republic (509 BC – 27 BC) 509 BC: Latins/Romans set up republic (citizens vote for leaders) Citizens free-born males in Rome CLASS CONFLICT Patricians- wealthy landowners with power Plebeians- farmers & workers can vote, but can’t rule Plebs vs. Pats Laws not written down Patrician judges stated & applied the law Plebeians went on strikes THE TWELVE TABLES 450 BC: Roman laws carved on 12 bronze tablets “innocent until proven guilty” - hung in Forum (public square) Senate (controlled $ & foreign policy) Dictator in emergencies 2 Consuls-1 yr. terms Assemblies voted on laws Elected tribunes who could veto senate Roman Religion Romans adopted Greek gods Jupiter: same as Greek god Zeus Juno: (Greek Hera) queen of the gods Diana: (Greek Artemis) goddess of the earth & hunters Minerva: (Greek Athena) goddess of wisdom & war Venus: (Greek Aphrodite) goddess of love Expansion 264 BC the city had taken over the Italian Peninsula Roman Legion=6,000 troops Disciplined- (decimation “removal of the tenth”) Roman roads- well constructed to move legions Rome vs. Carthage Carthage: wealthy trading city in north Africa that took Sicily Punic Wars (264-146 BC) st 1 Punic War (264 BC241 BC) Carthage tried to take Strait of Messina Carthage=strong navy; Rome=strong army Grappling hooks onto Carthaginian ships, boarded ships, & fought to the death Carthage gives up Sicily nd 2 Punic War (218 BC202 BC) Carthage wants revenge New general 25 years old--- Hannibal 218 BC- Hannibal takes Roman land in Spain Hannibal, 40,000 men, & 37 elephants invade through Alps 1/3 men die General Publius Scipio’s legions attack Zama (near Carthage) 202 BC: Scipio defeated Hannibal & Carthage gives up land in Spain 3rd Punic War (149 BC-146 BC) ROME DESTROYS CARTHAGE Burned Carthage Put salt in soil 130 BC—Rome ruled everything from Spain to Asia Minor Large area=hard to rule Divided into provinces who pay taxes (tribute) Tax collectors steal=rebellions Farmers move to city (farmland stolen while they were at Punic Wars) Slaves now doing work Poor farmers unemployed Tiberius & Gaius Gracchus (133 – 121 BC) Tribunes who made laws to help the poor Both killed in riots Gracchi Brothers Gaius Marius 107 BC—Elected consul Paid soldiers $ & land Soldiers loyal to commander 88 BC—Gaius overthrown by Lucas Cornelius Sulla (makes himself dictator) 1st Triumvirate Consuls—Gnaeus Pompey, Licinius Crassus, & popular general—Julius Caesar 60 BC—3 men = 1st Triumvirate (shared power) Jealous over power Pompey ordered Caesar to Rome Caesar crosses Rubicon River (with his army) & wins civil war Julius Caesar 45 BC—Dictator of Rome Gave grain to poor 44 BC—Dictator for life March 15, 44 BC (Ides of March)—Stabbed to death by Roman Senators 2nd Triumvirate Caesar’s 19 yr old grandnephew— Octavian—with—Marc Antony & Marcus Lepidus Antony moved to Egypt & married Cleopatra Oct. convinced Senate to declare war on Antony & Cleo. Octavian Marc Antony Marcus Lepidus Antony and Cleo. commit suicide Octavian=1st Roman Emperor st 1 Emperor 1. Augustus (Octavian): (27 BC-14 AD) Pax Romana begins Chief priest---head of state religion Had no sons Bad Emperors 2. Tiberius (14 AD-37 AD) Adopted son of Augustus Bad Emperors 3. Caligula (37 AD-41 AD) Tiberius’ grandnephew Unstable/CRAZY after illness 41 AD: assassinated by one of his guards Bad Emperors 4. Claudius (41 AD-54 AD) Uncle of Caligula Murdered by his wife- wanted her son to be emperor 5. Nero (54 AD-68 AD) Claudius’ stepson Bad Cruel & vain Murdered mom & wife-feared they’d kill him Sentenced to death by Senate; but, he committed suicide Emperors Senate Good Emperors chose 1st of the good emperors—Nerva (96-98 AD) Hadrian Hadrian’s Wall across Britain Marcus Aurelius 180 AD—last good emperor (Pax Romana ENDED) Army busy with civil wars=NOT defending borders Hadrian’s Wall Roman Civilization Pax Romana (27 BC-180 AD) “Roman Peace” allowed trade to grow Grain, wine, oil, cloth, pottery, glassware African ivory, Chinese silk, Indian pepper Roman Architecture Colosseum: Gladiator events Circus Maximus: Chariot races Pantheon: Temple to all gods Aqueducts: Artificial channels for carrying water Language Latin=language until 1500s Basis of Europe for Romance languages (French, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Romanian) Jewish Rebellions 6 AD: Kingdom of Judah added to Empire- renamed Judea Jews rebelled twice 66 & 135 AD Romans destroyed all but Western Wall of 2nd temple & forced Jews out of Jerusalem Jesus of Nazareth Jesus received Jewish education Jesus said God was loving & forgiving not harsh as Jews thought Disciples—believed Jesus was messiah (savior) Many Jews didn’t believe Jesus was messiah—this is difference between Christianity & Judaism Age 33 Jesus crucified Resurrection=way to prove Jesus was “Son of God” Leading Apostle—Paul Spread Christianity throughout Roman Empire Wrote epistles to churches (New Testament) Persecution Christians DID NOT honor emperor as a god Thrown into gladiator events to die 300s AD, many turn to Christianity Empire was about to collapse Early Church hierarchy (levels of authority) Lowest- parish priests & their parishes Many parishes together form a diocese which was overseen by a bishop Bishops interpreted beliefs, managed church property, & gave aid to the poor The most powerful bishops were archbishops who governed Christian in the large cities 5 archbishops of Rome, Constantinople, Alexandria, Antioch, & Jerusalem were called patriarchs Patriarch of Rome proclaimed authority over all Pope (head over all the churches) East didn’t accept the pope Western Church=Roman Catholic Church Eastern Church=Eastern Orthodox Church Hierarchy of the Roman Catholic Church 1. Pope 2. Archbishop 3. Bishop 4. Parish Priest Fall of the Western Empire 1.) Diocletian (284-307) Divided empire into 2 parts—East & West Issued Edict of Prices to slow inflation Diocletian Fall of the Western Empire 2.) Constantine (312-337) Won civil war Moved capital to Byzantium & renamed it Constantinople 1st Christian emperor – Edict of Milan Constantine Fall of the Western Empire 3.) Theodosius (337-395) Won civil war Will created separate empires with separate rulers East—Byzantine Empire West—Roman Empire Made Christianity official religion of empire Theodosius Fall of the Western Empire Civil wars caused : Difficult travel & trade Destroyed farmland—food prices increased Inflation (prices go up, value of $ goes down) Fall of the Western Empire Germanic Invasions 300s AD: Germanic tribes Looking for better climates & grazing lands Wanted to share Rome’s wealth Running from the Huns Fall of the Western Empire Visigoths & Vandals invaded & sacked Rome Franks & Goths divided Gaul Attila the Hun attacked Italy 453—Attila died & the Huns retreated into Eastern Europe 476—Roman emperor killed by Germanic soldier— Odoacer who made himself king of Italy 476—Date of the end of the Western (Roman) Empire Eastern Empire (Byzantine Empire) continued on for 1000 more yrs.