* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Immunity AIM: How does the immune system protect the body
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant disease resistance wikipedia , lookup
Duffy antigen system wikipedia , lookup
Atherosclerosis wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Plasmodium falciparum wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Anti-nuclear antibody wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Schistosoma mansoni wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
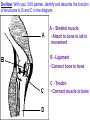
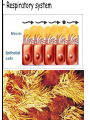
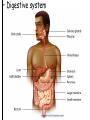
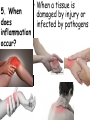
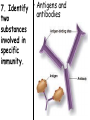
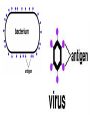
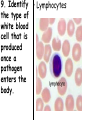
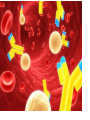
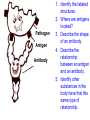
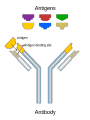
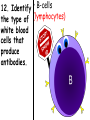
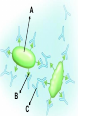
Topic: Immunity Aim: Describe the structure and role of pathogens in causing disease. Do Now: 1. Pass up your science fair data and conclusions. 2. Take out your immune system reading notes. 3. Take out your numbers! 4. Locomotion review with your 3:00 partner (next slide) HW: Read pgs. 655 and 656. Write a paragraph of at least 4 sentences explaining the difference between passive and active immunity. Due Wednesday: CL for Skeletal and Muscular Systems Muscle Fatigue Lab due Wednesday. Do Now: With your 3:00 partner, identify and describe the function of structures A, B and C in the diagram. A – Skeletal muscle •Attach to bone to aid in movement B - Ligament •Connect bone to bone C - Tendon •Connect muscle to bone Schistosoma mansoni is a major parasitic pathogen that causes schistosomiasis. You can become infected when your skin comes in contact with contaminated freshwater. Schistosomiasis accounts for greater than a ¼ of a million deaths per year. These not found in the U.S. Why? Within days after becoming infected, they may develop a rash or itchy skin. Within 1-2 months of infection, symptoms may develop including fever, chills, cough, and muscle aches. Symptoms of chronic schistosomiasis include: abdominal pain, enlarged liver, blood in the stool or blood in the urine, problems passing urine, and increased risk of bladder cancer. 1. Identify the name of diseasecausing organisms. • Pathogen • Prefix??? –From Greek pathos "disease” • Suffix??? –From French -génique "producing" 2. Identify some examples of these diseasecausing organisms. • Viruses • Bacteria • Fungi 3. Describe • It works against specific pathogens. the function of the immune system. 4. What does your body’s first line of defense consist of? • Skin • Respiratory system • Digestive system 5. When does inflammation occur? • When a tissue is damaged by injury or infected by pathogens • Redness 6. Identify • Temperature some signs increases of • Swelling inflammation. • Pain 7. Identify • Antigens and antibodies two substances involved in specific immunity. • On the surface of 8. Where pathogens are antigens (proteins) found? 9. Identify • Lymphocytes the type of white blood cell that is produced once a pathogen enters the body. 10. Identify • T-cells two types of • B-cells lymphocytes. • Antibodies 11. Identify the protein that is produced once an antigen enters the body A Pathogen Antigen B Antibody C 1. Identify the labeled structures. 2. Where are antigens located? 3. Describe the shape of an antibody. 4. Describe the relationship between an antigen and an antibody. 5. Identify other substances in the body have that this same type of relationship. • B-cells 12. Identify the type of (lymphocytes) white blood cells that produce antibodies. • They attach to antigens 13. Describe and make them useless. how • Attach to antigens that antibodies fit with their shape. are specific. 14. Describe • the function • of memory cells. Another type of lymphocyte Remain in the blood ready the defend against invasion of the same pathogen at another time Let’s summarize… 1. Explain what a pathogen in. 2. Explain the difference between an antigen and an antibody. 3. Explain what occurs when a foreign antigen enters the body. Which substances may form in the human body due to invaders entering the blood? a. nutrients b. vaccines c. antibodies d. red blood cells A B C Which phrase does not describe a way the human body responds to fight disease? a. destruction of infectious agents by white blood cells b. production of antibodies by white blood cells c. increased production of white blood cells d. production of pathogens by white blood cells Which statement does not identify a characteristic of antibodies? a. They are produced by the body in response to the presence of foreign substances. b. They may be produced in response to an antigen. c. They are nonspecific, acting against any foreign substance in the body. d. They may be produced by white blood cells. Which statement best describes an immune response? a. It always produces antibiotics. b. It usually involves the recognition and destruction of pathogens. c. It stimulates asexual reproduction and resistance in pathogens. d. It releases red blood cells that destroy parasites. Part of the body’s first line of defense against disease-causing organisms is a. the immune system b. the skin c. antibodies d. interferon Molecules that are foreign to your body are called a. antibodies b. white blood cells c. antigens d. histamines A(n) __ is a substance made by an organism in response to invading substances and disease-causing organisms. a. allergen b. antibody c. antigen d. pathogen The immune system of humans may respond to chemicals on the surface of an invading organism. 1. What are these chemicals on the surface called? 2. Explain what will happen once these chemicals enter the body. Which statement best describes an immune response? a. It always produces antibiotics. b. It usually involves the recognition and destruction of pathogens. c. It stimulates asexual reproduction and resistance in pathogens. d. It releases red blood cells that destroy parasites.