* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Anti-nuclear antibody wikipedia , lookup
Human leukocyte antigen wikipedia , lookup
Social immunity wikipedia , lookup
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Autoimmunity wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Duffy antigen system wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
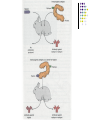
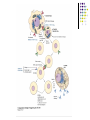
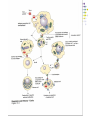
Antigens. Antigen structure of the microorganisms. Immune cells and their markers Antigen Antigen may be any non-self foreign substance to which lymphocytes respond Any antigen consists of: 1. Epitope 2. Non-specific remaining portion Classification: 1. Complete antigens 2. Haptens (complex and simple) Properties of the antigens Foreignness Antigenicity Specificity High molecular weight Solubility or colloidal properties Antigen specificity. 1. Heterogenic specificity 2. Species specificity. 3. Isospesificity. 4. Autospecificity Antigen structure of the bacterial cell O-Ag K-Ag H-Ag Vi-Ag Other bacterial antigens: Protective antigens Bacterial exotoxins and enzymes Specificity of bacterial antigens Genus antigens Species antigens Group specific antigens. Type specific antigens. Structure of the immune system Lymphoid system consist of the: Lymphoid cells (T and B cells) Lymphoid organs: 1. Central (primary) organs: thymus and bone marrow 2. Peripheral (secondary) lymphoid organs are: T-cells may be subdivided into some subsets (or subpopulation) due to their functions: 1. T- helper (TH) T- suppressor (TS) T- regulator (TR) T- cytotoxic (TC); Delayed-type hypersensitivity T cells (TDTH); 2. 3. 4. 5. B-cells Activated B-cells can differentiate into plasma or memory cells Cytokines 1. 2. 3. Monokines Lymphokines Interleukins (IL) Types of immune response Cellular immune response Humoral immune response Immunological memory Immunological tolerance Hypersensitivity reactions Immune response to an antigen may be of two broad types: The humoral or antibody mediated immunity (AMI). It is mediated by antibodies produced by plasma cell The cellular or mediated immunity (CMI). It is mediated by sensitized T-cells Cellular cooperation in the immune response 1. 2. 3. Antigen processing cells (APC) (macrophages or dendritic cells) TH cell (either Th1 or Th2) Either B-cell in the humoral immune response or TC (TK) cell in the cellular immune response