* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download the brain - Cloudfront.net
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
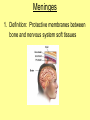
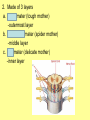
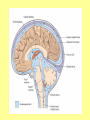
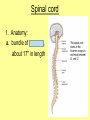
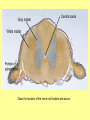
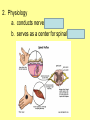
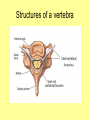
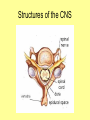
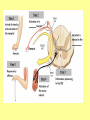
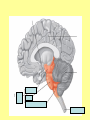
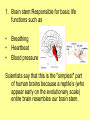
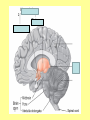
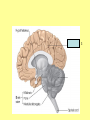
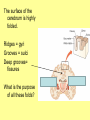
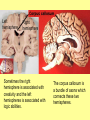
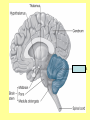
The Central Nervous System Upload 9.10 Central Nervous System Notes 1 Meninges 1. Definition: Protective membranes between bone and nervous system soft tissues 2. Made of 3 layers a. Dura mater (tough mother) -outermost layer b. Arachnoid mater (spider mother) -middle layer c. Pia mater (delicate mother) -inner layer Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) Read the definition. What structure of the nervous system is being described? 1. Definition: a clear watery liquid produced in the ventricles of the brain. Very Cool Demonstration -Put a raw egg in a container that is just a litter larger then the egg. -Cover and shake the container What happens to the egg? -Put a raw egg in a container full of water. -Cover and shake the container. What happens to the egg? What did the water represent? What functions of CSF were shown in the egg demo? Protection and Buoyancy Not shown: Removal of waste, Endocrine medium for the brain. Fun Fact Fun Fact: How much would a 165 lb person weigh if they were floating in CSF? 6 pounds Spinal cord 1. Anatomy: a. bundle of neurons, about 17" in length b. made of 2 types of tissue 1) gray matter- made of nerve cell bodies, neuroglial cells and blood vessels 2) white matter- made of axons c. consists of 31 segmentseach segment gives rise to a pair of spinal nerves Draw the location of the nerve cell bodies and axons. 2. Physiology a. conducts nerve impulses b. serves as a center for spinal reflexes Time for lab Find the spinal cord Structures of a vertebra Structures of the CNS THE BRAIN Upload 9.12 Central Nervous System Notes 2 DEFINITION: • The part of the CNS located within the skull • composed of 100 billion neurons and even more glia cells • weighs 3 pounds FUNCTION primary receiver, organizer and distributor of information for the body Can you put this in your own words? Spinal cord 1. Brain stem:Responsible for basic life functions such as • • • Breathing Heartbeat Blood pressure Scientists say that this is the "simplest" part of human brains because a reptile’s (who appear early on the evolutionary scale) entire brain resembles our brain stem. 2 1 Spinal cord Thalamus -interprets all senses except smell -synapses for voluntary movement Hypothalamus -controls the autonomic nervous system -coordinates the nervous and endocrine systems 3 Cerebrum (7/8 of human brain) Associated with higher brain functions such as thought and action. Divided into 4 lobes How do we know what each part of the cerebrum does? • MRI • Surgery Watch Amazing Medical Stories The surface of the cerebrum is highly folded. Ridges = gyri Grooves = sulci Deep grooves= fissures What is the purpose of all these folds? Folds increase surface area. Use the pictures to make an analogy. Left hemisphere Right hemisphere Sometimes the right hemisphere is associated with creativity and the left hemispheres is associated with logic abilities. The corpus callosum is a bundle of axons which connects these two hemispheres. 4 Cerebellum (Little brain) -associated with regulation and coordination of movement, posture, and balance What happens when our movements are not fine tuned? Link Just for fun Answer the rest of the questions on your sheet. 1. By the time you were born you lost _____ of the neurons you had as a fetus. A. 10% B. 25% C. 50% 2. As a teenager you ( lose / gain ) neurons as your body streamlines itself for optimal function. 3. Your brain is an energy hog. It occupies 2% of your body but uses _____ of your energy when you are at rest. A. 10% C. 50% B. 20% D. 75% 4. The more you repeat something the more brain space is dedicated to it. For example, in musicians the part of the brain that controls fingers used to play an instrument is up to 130% larger than in a non-musician. True or False? 5. Once you learn a task your brain shuffles it to a lower level of consciousness to save energy. If you move it into a conscious level you may make a mistake. True or False? 6. Stress can shrink your brain. True or False? Brain Health 7. Caffeine 8. Glucose 9. A healthy breakfast (whole grains, dairy, fruit) 10. Fish 11. Nuts and chocolate 12. Avocados and whole grains 13. Blueberries A. Perform better than your peers by increasing short-term memory and attention B. Eat 2 servings a week to gain omega 3 fatty acids for proper brain development and enhanced memory C. Protect your brain from free-radicals and increase your ability to learn D. Contain antioxidants that prevent cognitive decline E. In small quantities can boost energy and help you focus F. Get the blood flowing to the brain with these foods G. Offers short-term boost to memory, thinking processes, and mental ability In addition to eating healthy… 1. 2. 3. 4. Get a good nights sleep Stay hydrated Exercise Reduce stress