* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Huffman PowerPoint Slides
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Experimental psychology wikipedia , lookup
Trans-species psychology wikipedia , lookup
Music psychology wikipedia , lookup
Cross-cultural psychology wikipedia , lookup
International psychology wikipedia , lookup
Subfields of psychology wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
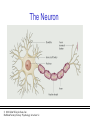
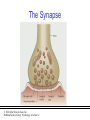
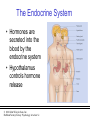
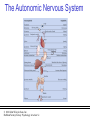
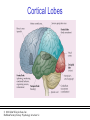
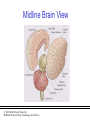
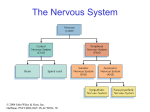
PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 2: The Biological Bases of Behavior Paul J. Wellman Texas A&M University Psychology in Action, Fifth Edition by Karen Huffman, Mark Vernoy, and Judith Vernoy © 2000 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman/Vernoy/Vernoy: Psychology in Action 5e Lecture Overview • • • • • Neurons Neurotransmitters and Hormones The Peripheral Nervous System The Brain Methods Used to Study the Brain © 2000 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman/Vernoy/Vernoy: Psychology in Action 5e Neurons • Neurons are cells that transmit information • Neurons are composed of: – Cell body – Dendrites: extensions that receive information – Axon: extends from cell body, carries electrical potential, sends a chemical message to adjacent neurons © 2000 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman/Vernoy/Vernoy: Psychology in Action 5e The Neuron © 2000 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman/Vernoy/Vernoy: Psychology in Action 5e The Action Potential • The membrane of the axon carries an electrical charge: – The area inside the axon membrane is more negative than is the outside (termed the resting membrane potential) – The RMP is usually about -70 mV • Action potential occurs when the membrane potential rapidly shifts from -70 to +40 mV. © 2000 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman/Vernoy/Vernoy: Psychology in Action 5e The Action Potential © 2000 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman/Vernoy/Vernoy: Psychology in Action 5e Synapse • The synapse is the junction between an axon terminal and an adjacent dendrite • Neurotransmitters are released from the axon terminal in response to an action potential into the synapse – The molecules diffuse across the synapse – NT molecules interact with receptors to alter the potential of the membrane • May lead to an action potential in the adjacent cell © 2000 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman/Vernoy/Vernoy: Psychology in Action 5e The Synapse © 2000 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman/Vernoy/Vernoy: Psychology in Action 5e Action Potentials • AP’s are fixed in amplitude • An AP sweeps along the axon membrane at a constant velocity • Vary in frequency (a few per second to a max of 1000 per second) • Are “all or none” in nature (AP either occurs or it does not) • AP’s have a refractory period © 2000 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman/Vernoy/Vernoy: Psychology in Action 5e Psychoactive Drugs • Psychoactive drugs affect the nervous system to alter mood, emotion and thought • Psychoactive drugs act by – Releasing neurotransmitters • Amphetamine releases dopamine – Stimulating or blocking neuron receptors • Alcohol depresses neuron function © 2000 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman/Vernoy/Vernoy: Psychology in Action 5e The Endocrine System • Hormones are secreted into the blood by the endocrine system • Hypothalamus controls hormone release © 2000 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman/Vernoy/Vernoy: Psychology in Action 5e Peripheral Nervous System • The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) includes all nerves outside the brain and spinal cord – Somatic NS carries sensory messages to brain and motor commands to the muscles – Autonomic N.S. regulates automatic body functions (heart rate, breathing) • Sympathetic: “Fight or Flight” • Parasympathetic: Active during digestion © 2000 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman/Vernoy/Vernoy: Psychology in Action 5e The Autonomic Nervous System © 2000 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman/Vernoy/Vernoy: Psychology in Action 5e Central Nervous System • The CNS is composed of the brain and spinal cord • Spinal cord connects the brain with the PNS – Comprised of cell bodies and axons that carry messages • Afferent: toward the brain • Efferent: away from the brain © 2000 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman/Vernoy/Vernoy: Psychology in Action 5e Overview of Brain © 2000 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman/Vernoy/Vernoy: Psychology in Action 5e Cerebral Cortex • Cortex refers to the outer covering of the brain – Consists of 2 hemispheres (left and right) • Cortex is divided into lobes – The lobes carryout different functions • • • • Frontal: Self awareness and planning Parietal: Body sensations Occipital: Vision Temporal: Hearing © 2000 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman/Vernoy/Vernoy: Psychology in Action 5e Cortical Lobes © 2000 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman/Vernoy/Vernoy: Psychology in Action 5e Subcortical Brain Areas • Corpus callosum: band of axons that interconnects the 2 hemispheres • Thalamus: sensory relay area • Limbic system: involved in emotionality • Hypothalamus: feeding, fleeing, mating, and fighting • Cerebellum: involved in motor control © 2000 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman/Vernoy/Vernoy: Psychology in Action 5e Midline Brain View © 2000 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman/Vernoy/Vernoy: Psychology in Action 5e Brainstem • Brainstem: primitive portion of brain – Pons – Medulla – Reticular activating system © 2000 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman/Vernoy/Vernoy: Psychology in Action 5e Studying the Brain • Neuroscientists learn about the function of the brain via: – Lesion studies: a brain region is destroyed and behavior is observed • Lesions of hypothalamus---> overeating – Electrical Recording: overall brain wave activity is monitored by the EEG – Imaging techniques allow the living brain to be studied for its activity during behavior © 2000 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman/Vernoy/Vernoy: Psychology in Action 5e Copyright Copyright 2000 by John Wiley and Sons, New York, NY. All rights reserved. No part of the material protected by this copyright may be reproduced or utilized in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying, recording, or by any information storage and retrieval system, without written permission of the copyright owner. © 2000 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Huffman/Vernoy/Vernoy: Psychology in Action 5e