* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Figure 2.25
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Trans-species psychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Music psychology wikipedia , lookup
Cross-cultural psychology wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Subfields of psychology wikipedia , lookup
International psychology wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
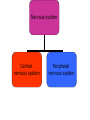
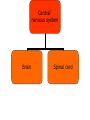
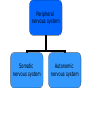
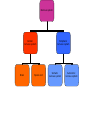
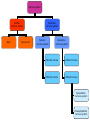
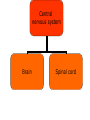
The Nervous System The Lay of the Land Nervous system Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Central nervous system Brain Spinal cord Peripheral nervous system Somatic nervous system Autonomic nervous system Nervous system Central nervous system Brain Spinal cord Peripheral nervous system Somatic nervous system Autonomic nervous system Figure 2.2 The human nervous system Klein/Thorne: Biological Psychology © 2007 by Worth Publishers Nervous system Central nervous system Brain Spinal cord Peripheral nervous system Somatic nervous system Autonomic nervous system Afferent nerves Afferent nerves Efferent nerves Efferent nerves Sympathetic nervous system Parasympathetic nervous system Generally speaking… • Sympathetic nervous system – Gets body ready for “fight or flight” • Parasympathetic nervous system – Saves energy, slows things down to normal after danger is over Protecting the Central Nervous System Figure 2.12 Structures that protect the CNS Klein/Thorne: Biological Psychology © 2007 by Worth Publishers Meninges: Layers of protection • Dura mater (tough mother) • Arachnoid mater (spiderweblike membrane) • Pia mater (pious mater) Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) • Water bed • Central canal • Cerebral ventricles Figure 2.14 The ventricular system Klein/Thorne: Biological Psychology © 2007 by Worth Publishers The Blood-Brain Barrier • Prevents harmful substances in the blood from entering the brain • The cells that make up the walls of the blood vessel walls are squeezed close together, so many molecules cannot pass through The Blood-Brain Barrier • Substances that are important for brain and body functioning can pass through • Psychotropic drugs, anti-histamines Cells of the Nervous System Cells of the Nervous System • Neurons • Glial cells Neurons Figure 2.5 A typical neuron and synapse Klein/Thorne: Biological Psychology © 2007 by Worth Publishers Figure 2.6 The four major types of synapses Klein/Thorne: Biological Psychology © 2007 by Worth Publishers 2. Glial cells • Oligodendrocytes – Myelin sheath of central nervous system • Schwann cells – Myelin sheath of peripheral nervous system Figure 2.9 Types of glial cellsS Klein/Thorne: Biological Psychology © 2007 by Worth Publishers 2. Glial cells • Astrocytes – Astro = star – Helps maintain the blood-brain barrier – Provide neurons with nutrients – Support neurons: protect and hold neurons in place – Keep neurons separated to prevent messages from being mistakenly transmitted 2. Glial cells • Microglial – Micro = small – Clean up neurons that have died Central nervous system Brain Spinal cord The Spinal Cord • 31 pairs of spinal nerves – – – – – 8 cervical 12 thoracic 5 lumbar 5 sacral 1 coccygeal Figure 2.10 The 31 pairs of spinal nerves Klein/Thorne: Biological Psychology © 2007 by Worth Publishers Gray matter: cell bodies White matter: axons Figure 2.15 Section of the spinal cord Klein/Thorne: Biological Psychology © 2007 by Worth Publishers Figure 1.3 A cross-sectional view of part of the spinal cord Klein/Thorne: Biological Psychology © 2007 by Worth Publishers • Dorsal, afferent, sensory • Ventral, efferent, motor Major Structures of the Brain Major Structures of the Brain • Hindbrain • Midbrain • Forebrain Major Structures of the Brain • Hindbrain Figure 2.17 The hindbrain Klein/Thorne: Biological Psychology © 2007 by Worth Publishers Hindbrain • Medulla • Pons • Cerebellum • Medulla • Vital functions (heart beat, breathing) • Swallowing, coughing, sneezing • Pons • Relays info between cerebellum and forebrain • Sleep • Levels of consciousness • Cerebellum • Balance • Motor function • Movement • Posture Major Structures of the Brain • Midbrain Figure 2.18 The midbrain Klein/Thorne: Biological Psychology © 2007 by Worth Publishers Midbrain • Periaqueductal gray • Substantia nigra • Periaqueductal gray – Drugs that reduce pain • Substantia nigra – Latin for “black substance” – Dopamine Major Structures of the Brain • Forebrain • Thalamus • Hypothalamus • Cerebral cortex • Limbic system • Basal ganglia http://www.msnbc.msn.com/id/10401930 • Thalamus • Relays information from all senses except smell • Like a telephone switchboard that conveys information from vision, hearing, touch. Figure 2.21 The thalamus Klein/Thorne: Biological Psychology © 2007 by Worth Publishers • Hypothalamus – Controls release of hormones – that stimulate growth – when under stress • Controls temperature, hunger, thirst Figure 2.22 The hypothalamus Klein/Thorne: Biological Psychology © 2007 by Worth Publishers • The cerebral cortex Figure 2.25 The cerebral cortex Klein/Thorne: Biological Psychology © 2007 by Worth Publishers • Frontal lobe – – – – – Movement Memory Decision-making Emotion Conscious control of behavior – Personality Figure 2.25 The cerebral cortex Klein/Thorne: Biological Psychology © 2007 by Worth Publishers Damage to the frontal lobe • Difficulty with responding to the environment – Not following rules – Impaired learning • Changes in personality • Temporal lobe – Hearing – Memory – Language Figure 2.25 The cerebral cortex Klein/Thorne: Biological Psychology © 2007 by Worth Publishers • Parietal lobe – Information from touch – Making sense of spatial relationships in the environment Figure 2.25 The cerebral cortex Klein/Thorne: Biological Psychology © 2007 by Worth Publishers Damage to the parietal lobe • Right parietal lobe: neglect of left side • Occipital lobe – Vision Figure 2.25 The cerebral cortex Klein/Thorne: Biological Psychology © 2007 by Worth Publishers • The limbic system Figure 2.23 The limbic system Klein/Thorne: Biological Psychology © 2007 by Worth Publishers • Amygdala: fear and escape • Hippocampus: memory • The basal ganglia Figure 2.23 The basal ganglia Klein/Thorne: Biological Psychology © 2007 by Worth Publishers Basal ganglia • Voluntary movements – Parkinson’s disease – Huntington’s disease – Tourette’s Figure 2.4 Anatomical directions and perspectives Klein/Thorne: Biological Psychology © 2007 by Worth Publishers