* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nervous System 4/28/09
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
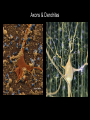
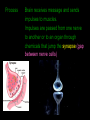
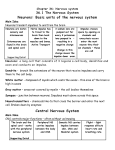
Nervous System 05/28/2013 pages 163-164 Know: What are the 3 functions of the nervous system? Evidence: TB pg 633, draw, color, and captions Functions 1. Receiving info – inside and outside body 2. Responding to info – reaction to stimulus (change/signal) 3. Maintaining homeostasis Process Neurons (nerve cells) carry nerve impulses (electrical or chemical messages) Process Impulses begin in dendrite, move toward cell body, then down axon. Dendrite Carries impulse toward cell body Axon Carries impulse away from cell body (Draw picture/label below) Axons & Dendrites Process Brain receives message and sends impulses to muscles. Impulses are passed from one nerve to another or to an organ through chemicals that jump the synapse (gap between nerve cells) Types 1. Central – control center of body, brain and spinal cord 2. Peripheral – carries impulses between central nervous system and rest of body - Somatic nervous system – controls voluntary actions (texting) - Autonomic n.s. – controls involuntary actions (heart beat) Reflex Automatic involuntary response to danger. Ex: your arm pulls back if you touch something hot Evidence & Summary Evidence: TB page 633, Draw, label, color