* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Placebo
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Emotion perception wikipedia , lookup
Types of artificial neural networks wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
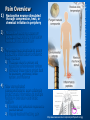
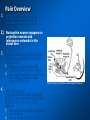
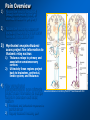
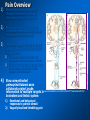
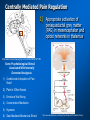
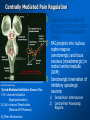
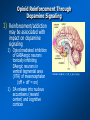
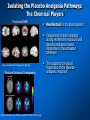
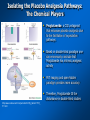
Placebos and Painkillers: Is Mind as Real as Matter? Luana Colloca and Fabrizio Benedetti 2005 in Nature Reviews Neuroscience http://www.annkullberg.com/Shows/2003/Hild.jpg Jess Benjamin Steele Taylor Celeste Parot January 30, 2008 http://www.scripps.edu/cb/patapoutian/nocisensor.jpg Pain Overview 1) Nociceptive neuron stimulated through compression, heat, or chemical irritation in periphery 2) Nociceptive neuron synapses on projection neurons and interneuron networks in the dorsal horn 3) Myelinated neospinothalamic axons project fine information to thalamic relay nucleus 1) 2) 4) Thalamus relays to primary and associative somatonsensory cortices Ultimately these regions project back to brainstem, prefrontal, limbic system, and thalamus Slow unmyelinated paleospinothalamic axon collaterals project crude information to multiple targets in brainstem and limbic system 1) 2) Emotional and behavioral responses to painful stimuli Vaguely localized throbbing pain http://www.laesieworks.com/spinal/pict/SpinalCord.jpg 1) Pain Overview Nociceptive neuron stimulated through compression, heat, or chemical irritation in periphery 2) Nociceptive neuron synapses on projection neurons and interneuron networks in the dorsal horn 3) Myelinated neospinothalamic axons project fine information to thalamic relay nucleus 1) 2) 4) Thalamus relays to primary and associative somatonsensory cortices Ultimately these regions project back to brainstem, prefrontal, limbic system, and thalamus Slow unmyelinated paleospinothalamic axon collaterals project crude information to multiple targets in brainstem and limbic system 1) 2) Emotional and behavioral responses to painful stimuli Vaguely localized throbbing pain www.nursece.com/onlinecourses/imagesPain/Fig2.gif 1) 2) Pain Overview Nociceptive neuron stimulated through compression, heat, or chemical irritation in periphery Nociceptive neuron synapses on projection neurons and interneuron networks in the dorsal horn 3) Myelinated neospinothalamic axons project fine information to thalamic relay nucleus 1) 2) 4) Thalamus relays to primary and associative somatonsensory cortices Ultimately these regions project back to brainstem, prefrontal, limbic system, and thalamus Slow unmyelinated paleospinothalamic axon collaterals project crude information to multiple targets in brainstem and limbic system 1) 2) Emotional and behavioral responses to painful stimuli Vaguely localized throbbing pain www.doctordeluca.com/Library/Pain/CP1NewDisease2K.htm 1) Pain Overview Nociceptive neuron stimulated through compression, heat, or chemical irritation in periphery 2) Nociceptive neuron synapses on projection neurons and interneuron networks in the dorsal horn 3) Myelinated neospinothalamic axons project fine information to thalamic relay nucleus 1) 2) Thalamus relays to primary and associative somatonsensory cortices Ultimately these regions project back to brainstem, prefrontal, limbic system, and thalamus 4) Slow unmyelinated paleospinothalamic axon collaterals project crude information to multiple targets in www.doctordeluca.com/Library/Pain/CP1NewDisease2K.htm brainstem and limbic system 1) 2) Emotional and behavioral responses to painful stimuli Vaguely localized throbbing pain Centrally Mediated Pain Regulation 1) Appropriate activation of periaqueductal grey matter (PAG) in mesencephalon and opioid networks in thalamus http://www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/288/5472/1769 Some Psychobiological Stimuli Associated With Internally Generated Analgesia: 1) Conditioned Anticipation of Pain Relief 2) Pain in Other Areas 3) Emotional Well Being 4) Concentration/Meditation 5) Hypnosis 6) Gate-Mediated Mechanical Stimuli http://www.doctordeluca.com/Library/Pain/Graphics/CP1NewDis-F2.bmp Centrally Mediated Pain Regulation 1) Appropriate activation of 2) (notice the inhibition of retrograde substance p release into the periphery!) http://www.mona.uwi.edu/fpas/courses/physiology/neurophysiology/P ainRapheFeedback.jpg Opiod-Mediated Inhibition Occurs Via: 1) K+ channel Activation (Hyperpolarization) 2) Ca2+ channel Deactivation (Reduced NT Release) 3) Other Mechanisms 3) periaqueductal grey matter (PAG) in mesencephalon occurs PAG projects into nucleus raphe magnus (serotonergic) and locus ceruleus (noradrenergic) in rostral ventral medulla (RVM) Serotonergic innervation of inhibitory opiodergic neurons 1) 2) Dorsal Horn Interneurons Central Pain Processing Regions 1) Opioid Reinforcement Through Dopamine Signaling Reinforcement/addiction may be associated with impact on dopamine signaling 1) Opiod mediated inhibition of GABAergic neurons tonically inhibiting DAergic neurons in ventral tegmental area (VTA) of mesencephalon (off + off = on) 1) DA release into nucleus accumbens (reward center) and cognitive cortices thebrain.mcgill.ca/.../i_03_cr_que_1a.jpg Isolating the Placebo Analgesia Pathways: The Chemical Players Functional MRI • Remfentanil is an opioid agonist • Comparison of brain imaging during remfentanil exposure and placebo-analgesia reveals similarities in the activated pathways www.ym.edu.tw/rcinn/images/cp1-fg3.png Positron Emission Tomography http://www.nida.nih.gov/NIDA_notes/NNVol16N2/Positron.jpg • This supports the opioid hypothesis of the placeboanalgesic response Isolating the Placebo Analgesia Pathways: The Chemical Players • Proglutamide: a CCK antagonist that enhances placebo analgesia due to the facilitation of expectation pathways • Based on double-blind paradigm one can erroneously conclude that Proglutamide has intrinsic analgesic activity • PET imaging and open-hidden paradigm provides more accuracy • Therefore, Proglutamide IS the disturbance in double-blind studies http://www.nature.com/nrn/journal/v6/n7/fig_tab/nrn1705_ F1.html Isolating the Placebo Analgesia Pathways: The Chemical Players • Naloxone is the prototypical opioid • antagonist (and OD antidote) Naloxone reliably blocks placebo induced analgesia – But, only through conditioning with previous opioid-analgesic responses – Non-opiod associated placebo effects are naloxone insensitive • Sumatriptan (5-HT agonist) • Therefore, naloxone also blocks side- effects accompanying opioid-operating placebo responses – Respiratory depression – Cardiac depression • Disturbance: In a double-blind study, naloxone appears to have a hyperalgesic effect (but not in openhidden paradigms)