* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Brain for Not-So
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of human intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Impact of health on intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
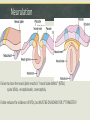
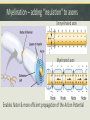
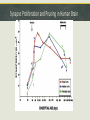
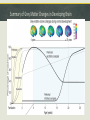
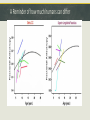
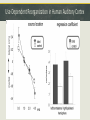
Week 2 – Normal Brain Dynamics Overview: Physical Development – growing a brain. “Fine Tuning” the brain – part of development that continues throughout life Aging – Maturation followed by (different degrees of) degeneration. Response to injury – restoration of function, or disorder. Timeline of neuron birth & death in brain development Neurulation Failure to close the neural plate results in “neural tube defects” (NTDs) spina bifida, encephalocele, anencephaly Folate reduces the incidence of NTDs, but MUST BE ON BOARD FOR 1st TRIMESTER! Apoptosis – “programmed cell death” - An “orderly” death and removal of a cell - As opposed to “necrotic” or injury-induced cell death (“messy”) - Important for proper neural tube formation - Also matches neuronal population to available targets - Eliminates neurons with erroneous or inadequate projections Myelination – adding “insulation” to axons Unmyelinated axon Myelinated axon Enables faster & more efficient propagation of the Action Potential Neurogenesis does not stop at birth Occurs in normal adult brain Adds neurons in hippocampus “ “ striatum Maybe also in cerebral cortex Neurogenesis is enhanced/supported by exercise Seems to be increased by antidepressant drugs Synapse “Pruning” Synapse Proliferation and Pruning in Human Brain Summary of Grey Matter Changes in Developing Brain A Reminder of how much humans can differ Ok , so we built a brain…what’s it do now?! The brain is “tuned” to its experience For certain functions/areas there is a “critical period” for “tuning” Imprinting Studied how newborns bond with parents He was first creature seen by newly-hatched geese They became “imprinted” with/by his appearance. Reason for naming of “baby duck syndrome” by computer software developers Konrad Lorenz The “Westermarck Effect” “Reverse Sexual Imprinting” Seen among non-related populations raised together E.g. Kibbutz System Out of the nearly 3,000 marriages that occurred across the kibbutz system, only fourteen were between children from the same peer group. Of those fourteen, none had been reared together during the first six years of life. Evolutionary advantage of reducing in-breeding Edvard Westermarck Harry Harlow – Maternal Bonding Investigated factors influencing newborn bonding to mother Experiment with infants growing up with 2 “surrogate mothers” One provided food, but was cold and hard (wire) The provided no nourishment, but was soft and warm Infants greatly preferred the “cloth mother” Retreated to the soft mother when anxious Were more outgoing, adventurous, able to meet new monkeys in presence of “cloth mother” Touch (e.g., “skin to skin”) now an important part of premature infant care. Effect of environment on synapse pruning & stabilization Development involves fine-tuning circuits ready for input NORMAL BIRTH 2 WEEKS 4 WEEKS 6 WEEKS VISUAL CORTEX LATERAL GENICULATE (THALAMUS) IF ONE EYE IS CLOSED The developing brain “tunes” to its environment Visual input alone is not sufficient – must coordinate with movement Passive exposure does not yield appropriate motor reponses Passive kittens do not learn: - Paw placement - How to recognize a “cliff” - Blink reflex “If you use it, your brain glues it” (?) Standard Cage Enrichced Cage Effects of Environmental Enrichment on the Brain SC IC Neuron Branching Standard Enriched Dendrite Structure EC “Enriched” environment = “Enriched” brain structure and function Use-Dependent Reorganization in Human Auditory Cortex