* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ppt - Komion
Gluten immunochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Anti-nuclear antibody wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Common cold wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Poliomyelitis eradication wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Vaccination policy wikipedia , lookup
Multiple sclerosis research wikipedia , lookup
Meningococcal disease wikipedia , lookup
Poliomyelitis wikipedia , lookup
Social immunity wikipedia , lookup
Whooping cough wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Polio vaccine wikipedia , lookup
Herd immunity wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
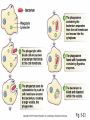
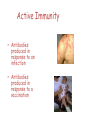
Immunisation 1796 If you understand basic immunology you can explain... • How vaccines work and why vaccine failures occur • Adverse events and their timing • Why the schedule is as it is • Why vaccines cannot overload the immune system Physical barriers • Skin – 2 m² • Mucosal membranes – digestive, respiratory, reproductive tract – 400 m² Innate immunity Phagocytosis Macrophage - WBC Rapid action 0-4 hours Non-specific – same response each time No memory – same response at each encounter • May destruct the antigen • • • • • Adaptive immunity • Second level of defence • Effectiveness increases with each encounter • Specific immune response Types of (adaptive) immunity • Active Immunity • Passive Immunity Passive Immunity • Transfer of maternal antibodies • Administration of antibodies Active Immunity • Antibodies produced in response to an infection • Antibodies produced in response to a vaccination Types of antibody • IgG – the only type that crosses the placenta (after 32 weeks) • IgA – in breast milk – gives some mucosal protection • IgE – over production associated with anaphylaxis • Also IgM – maybe further reading! Active versus passive immunity • ACTIVE • PASSIVE • Long lasting • Only short term • Takes time to be effective • Immediate protection • http://www.nhs.uk/Video/Pages/Vaccinationa nimation2.aspx Vaccination schedule 2015 Age Diseases protected against 2 months Diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough, polio, Hib, pneumococcal disease Rotavirus (Men B from Sept 2015) 3 months Diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough, polio, Hib, meningococcal disease type C and Rotavirus 4 months Diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough, polio, Hib, pneumococcal & (Men B from Sept 2015) 12-13 months Hib/meningococcal disease type C pneumococcal disease Measles, mumps & rubella (MMR) and (Men B from Sept 2015) 2,3 &4yrs Children’s flu vaccine 3yrs 4m Diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough, polio MMR (pre-school immunisations) 12-13yrs HPV (cervical cancer) girls only 2 x doses 6 months apart 13-18yrs Diphtheria, tetanus, polio (school leavers immunisations) Men ACWY 17 Vaccine overload? Part of body Bacteria Scalp 1,000,000/cm2 Surface of skin 1000/cm2 Saliva 100,000,000/g Nasal mucus 10,000,000/g Faeces Over 100,000,000/g Contraindications • • • • • Immunosuppression & treatment Some steroid use Unstable neurological condition Previous anaphylactic reaction Care with live vaccines • Pyrexia • Acute illness • Side effects?? Vaccine trials • • • • • Pre-clinical laboratory based work Phase I – (small scale – adults) Phase II – (population specific) Phase III – (100s-1000s participants) Phase IV vaccines – MHRA reporting Getting to the schedule • • • • • • Research and development JCVI Recommendations to DH Cost and feasibility studies Supply and delivery Awareness and training issues References/further reading • Immunisation against infectious disease (Green Book) [online] https://www.gov.uk/government/organisation s/public-health-england/series/immunisationagainst-infectious-disease-the-green-book • Public Health England website https://www.gov.uk/government/organisation s/public-health-england