* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download protein synthesis
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
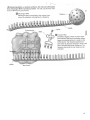
Biology Unit 4B Name: _______________________ GN#2: Protein Synthesis Proteins are biomolecules that regulate cell processes. o Examples: Enzymes, Transport Proteins, Hemoglobin o Made of (Monomer) = Amino Acids assembled at a Ribosome 2 Steps to Make a Protein o 1) DNA to mRNA Transcription o 2) mRNA to Protein Translation Transcription DNA “rewritten” as mRNA….must be done because DNA is too large to leave the nucleus. o Steps Involved 1. Helicase enzymes unzip DNA by breaking hydrogen bonds between nitrogen bases 2. RNA nucleotides are added to match the DNA template 3. New mRNA detaches from the DNA template 4. mRNA is edited to remove Introns (Junk DNA – don’t code for proteins) and leave the Exons (Expressed DNA) DNA Intron Pre-mRNA mRNA Exon 5. mRNA leaves the nucleus & travels to the ribosome Practice the process of Transcription below DNA TAC GGA AGG TTT ACT mRNA Translation mRNA used to determine Amino Acid sequence (Protein) o Steps Involved 6. mRNA attaches to ribosome 7. Ribosome reads mRNA nucleotides in sets of 3 called a Codon 8. A Start Codon (AUG) is found & amino acids are delivered to ribosome by tRNA 9. Amino acids are joined together with peptide bonds until a Stop Codon (UGA, UAA, UAG) is found 10. Assembled protein is released from ribosome, folded & travels out into the cell to perform a specific function 1 Genetic Code Chart used to determine the amino acid written into the mRNA code. Cross reference letters to determine the correct amino acid. Practice using the genetic code to determine the correct amino acid sequence DNA TAC GGA AGG TTT ACT mRNA Amino Acid 2 You should be able to label the diagram above. I II III IV V What process is this? Where does it happen? 3 4