* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Faber: Sequence resources
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Segmental Duplication on the Human Y Chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Transposable element wikipedia , lookup
DNA sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Sequence alignment wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular Inversion Probe wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Whole genome sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Human Genome Project wikipedia , lookup
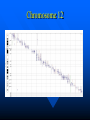
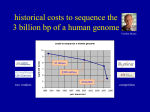
Methods in genome sequencing and SNP finding Gabor Marth BI 820 presented by Tony Faber Sequences used in SNP analysis and genomic sequencing Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs) Sequence-tagged site (STS) sequences Reduced Representation Libraries (RRL) Whole-genome shotgun libraries Genome Survey Sequence (GSS) Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs) Relatively short (200-400bp) of partial cDNA sequences Many are single-pass reads from tissue specific cDNA libraries HGP aligned to human reference sequence EST quality (SEQREF) Coding and UTRs make up ESTs (can be multiple exons) Identifying putative full-ORF cDNA clones 5’ ESTs Matches Refseq No Yes Read page 2 5’ end aligns at start no Yes Protein Comp Matches Aminoterminus HKScan GenomeScan Comparision Matches 5” end of predicted gene Select for complete sequencing Sequenced Tagged Sites (STSs) First used- advantages include PCR primers readily available, recovered BACs/YACs during HGP PCR much cheaper than BAC/YAC sequencing Represent the superposition (i.e. can also be double-pass reads) Fingerprint clone contigs bound to specific STSs Whole-genome shotgun • Random clones from the genomes of many individuals • Requires several-fold coverage of the genome (e.g. sequencing, SNP discovery) Genome Survey Sequence (GSS) To survey a new genome, or get a general idea of genomic make-up of organism Similar to ESTs, except the DNA is genomic in origin (not mRNA) Also single pass reads From cosmid/BAC/YAC ends, exon trapped genomic sequences, and Alu PCR sequences Splicing events Reduced Representation sequences (RRS) Heavy cloning in certain regions Contain STSs, many corresponding to genes or ESTs One clone per MB on every chromosome, excellent coverage Reproducibly prepared subsets of the genome from several individuals, each containing a manageable number of loci Thus allowing Re-sampling Greater flexibility and efficiency Problems- creating reduced representations, finding ortholouges matches, accuracy Origin of replication Binding to particular protein Restriction fragments in a certain range (size selected restriction fragments) Chromosome 12 SNP context • Most popular method for obtaining SNP’s •EST alignment •Major sources of genomic SNPs include sequences for restricted genome representation libraries, random shotgun reads aligned to genome sequence, BAC/YAC overlaps