* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download RNA Polymerase II mediated modifications
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of depression wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
DNA methylation wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Histone acetyltransferase wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
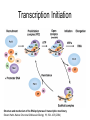
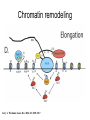
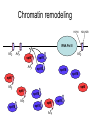
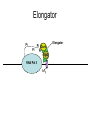
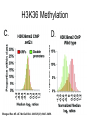
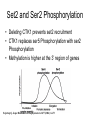
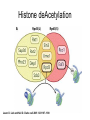
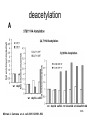
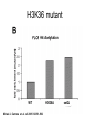
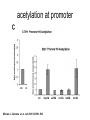
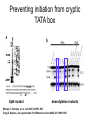
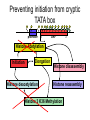
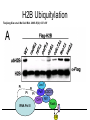
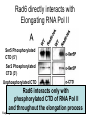
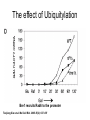
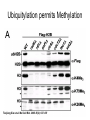
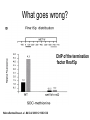
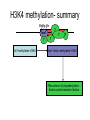
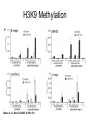
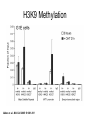
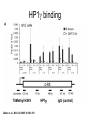
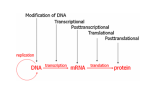
RNA Polymerase II mediated modifications What RNA Pol II does to histones and why? Asaf Peer Seminar in Computational Biology, 2007 histones • Histones pack the DNA • exposed to posttranslational modifications • some modifications are abundant than other Histones • The existence of a “histone code” is controversial • modifications marks heterochromatin, especially Methylation of K9, K27 of H3 • marks active genes with acetylation in the promoter region • Phosphorylation of ser10 H3 correlates with mitosis Transcription Initiation Structure and mechanism of the RNA polymerase II transcription machinery Steven Hahn. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology 11, 394 - 403 (2004) Transcription Elongation http://www.smbs.buffalo.edu/bch/images/figures/ponticelli_fig.jpg Modifications in Elongation • Control Chromatin remodeling • Recruitment of elongation and termination factors • Prevent initiation from within the gene Chromatin remodeling • • Evidence: - Chromatin lost in highly transcribed genes - accumulation of H3.3 in highly transcribed genes Finding: - histones are evicted and replaced during elongation Jerry L. Workman Genes Dev. 2006; 20: 2009-2017 Chromatin remodeling Jerry L. Workman Genes Dev. 2006; 20: 2009-2017 Chromatin remodeling H3/H4 H2A/H2B RNA Pol II Ac Ac Ac spt6 Ac spt16 spt16 spt16 spt16 spt6 Ac spt6 spt6 spt16 Ac spt16 spt16 spt6 Ac spt16 Histone Acetylation • Acetylation may facilitate the disassembly of nucleosomes • It may also facilitate their reassembly • Acetylation is done using Gcn5 and Elp3 • In hypoacetylated genes expression level is reduced • Mutations in spt6/spt16 with mutations in gcn5/elp3 has an alleviating effect Svejstrup Q. Jesper Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1677 (2004) 64-73 Elongator Pi Pi Pi Gcn5 Pi Elp3 RNA Pol II Ac Elongator H3K36 Methylation • Lys 36 of Histone H3 is hypermethylated • apparently, set2 has to do with the methylation Bhargavi Rao et. al. Mol Cell Biol. 2005 25(21): 9447–9459. Nevan J. Krogan et. al. Mol Cell Biol. 2003 23:4207-4218 Set2 and Ser2 Phosphorylation • Deleting CTK1 prevents set2 recruitment • CTK1 replaces ser5 Phosphorylation with ser2 Phosphorylation • Methylation is higher at the 3’ region of genes Svejstrup Q. Jesper Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1677 (2004) 64-73 The role of H3K36 Methylation Conflict Histone deAcetylation • Rpd3- histone deacetylase • found in the complexes Rpd3(L) and Rpd3(S) • The complexes share the proteins Rpd3, Sin3 and Ume1 • What are the differences between the two complexes? Histone H3 methylation by Set2 directs deacetylation of coding regions by Rpd3S to suppress spurious intragenic transcription. Michael J. Carrozza, Bing Li, Laurence Florens, Tamaki Suganuma, Selene K. Swanson, Kenneth K. Lee, WeiJong Shia, Scott Anderson, John Yates, Michael P. Washburn and Jerry L. Workman Cell. 2005 123(4):581-92. Histone deAcetylation Jason D. Lieb and Neil D. Clarke cell 2005 123:1187-1190 deacetylation wt dep1Δ eaf3Δ rco1Δ set2Δ sin3Δ eaf3chdΔ wt dep1Δ eaf3Δ rco1Δ set2Δ sin3Δ eaf3chdΔ wt dep1Δ eaf3Δ rco1Δ set2Δ sin3Δ eaf3chdΔ Michael J. Carrozza et. al. cell 2005 123:581-592 H3K36 mutant WT Michael J. Carrozza et. al. cell 2005 123:581-592 H3K36A set2Δ acetylation at promoter wt dep1Δ eaf3Δ rco1Δ wt Michael J. Carrozza et. al. cell 2005 123:581-592 set2Δ dep1Δ sin3Δ eaf3Δ rco1Δ set2Δ sin3Δ Preventing initiation from cryptic TATA box Spt6 mutant deacetylation mutants Michael J. Carrozza et. al. cell 2005 123:581-592 Craig D. Kaplan, Lisa Laprade and Fred Winston science 2002 301:1096-1099 Preventing initiation from cryptic TATA box promoter 5’ ORF 3’ Histone Acetylation Initiation Elongation Histone disassembly Histone deacetylation Histone reassembly Histone 3 K36 Methylation H3K4 Methylation and H2B Ubiquitylation Histone H2B Ubiquitylation Is Associated with Elongating RNA Polymerase II Tiaojiang Xiao, Cheng-Fu Kao, Nevan J. Krogan, Zu-Wen Sun, Jack F. Greenblatt, Mary Ann Osley, and Brian D. Strahl Mol.Cell biol. 2005 25(2):637-651 H2B Ubiquitylation • H2B goes ubiquitylation in transcribed genes at lysine 123 • It has to do with H3 methylation on lysine 4 and 79 • In the promoter region H2B goes ubiquitylation which is rapidly removed by ubp8 H2B Ubiquitylation Tiaojiang Xiao et.al. Mol Cell Biol. 2005 25(2): 637–651 Pi Leo1 Pi Pi Pi Paf1 Ctr9 RNA Pol II CDC73 Rtf1 Rad6 Ub Rad6 directly interacts with Elongating RNA Pol II Ser5 Phosphorylated CTD (5’) Ser2 Phosphorylated CTD (3’) Unphosphorylated CTD Rad6 interacts only with phosphorylated CTD of RNA Pol II and throughout the elongation process Tiaojiang Xiao et.al. Mol Cell Biol. 2005 25(2): 637–651 The effect of Ubiquitylation Bre1 recruits Rad6 to the promoter Tiaojiang Xiao et.al. Mol Cell Biol. 2005 25(2): 637–651 Ubiquitylation permits Methylation Tiaojiang Xiao et.al. Mol Cell Biol. 2005 25(2): 637–651 Elongation- Gal1 paradigm H3K4 Methylation • Lysine 4 of Histone 3 is being Methylated by set1 • set1 interacts with Ser5 phosphorylated CTD RNA Pol II • Therefore, H3K4 is hypermethylated at the 5’ regions of active genes • As we will see, some factor binds di and tri Methylated H3K4 residues Methylation of Histone H3 K4 Mediates Association of the Isw1p ATPase with Chromatin Helena Santos-Rosa, Robert Schneider, Bradley E. Bernstein, Nickoletta Karabetsou, Antonin Morillon, Christoph Weise, Stuart L. Schreiber, Jane Mellor and Tony Kouzarides Molecular Cell 2005,12:1325-1332 Isw1 binds Methylated H3K4 Nevertheless, Isw1 can bind chromatin in alternative ways! Helena Santos-Rosa et. al. Mol Cell 2003 12:1325-1332 Set1 and Isw1- the MET16 paradigm Helena Santos-Rosa et. al. Mol Cell 2003 12:1325-1332 What goes wrong? Poly(A) mRNA level Helena Santos-Rosa et. al. Mol Cell 2003 12:1325-1332 What goes wrong? RNAPII in the mutant is more abundant in the 3’ region maybe the termination process gets stuck? Helena Santos-Rosa et. al. Mol Cell 2003 12:1325-1332 What goes wrong? ChIP of the termination factor Rna15p Helena Santos-Rosa et. al. Mol Cell 2003 12:1325-1332 H3K4 methylation- summary MeMe Me Isw1 ? Set1 methylates H3K4 ? ?ORF ? ? Isw1 binds methylated H3K4 Recruitment of ployadenylation factors and termination factors For ending- a mystery H3K9Me- What are you saying? Histone H3 Lysine 9 Methylation and HP1γ Are Associated with Transcription Elongation through Mammalian Chromatin Christopher R. Vakoc, Sean A. Mandat, Benjamin A. Olenchock and Gerd A. Blobel Molecular Cell 2005,19(3):381-391 H3K9 Methylation • H3K9 Methylation is known to mark heterochromatin • HP1 protein binds di and tri-methyl H3K9 and takes a part in gene silencing • In Mammals, 3 types of HP1 are found: HP1α HP1β and HP1 H3K9 Methylation • G1E cells were used • These cells are arrested in their differentiation due to lack in GATA-1 transcription factor • GATA-1 fused to Estrogen receptor was expressed • Estrogen controls the differentiation and makes it fast and synchronized H3K9 Methylation Vakoc et. al. Mol Cell 2005 19:381-391 H3K9 Methylation Vakoc et. al. Mol Cell 2005 19:381-391 HP1 binding TriMethyl H3K9 Vakoc et. al. Mol Cell 2005 19:381-391 HP1 IgG (control) Conclusions • Acetylation is important for Chromatin disassembly and reassembly • Methylation of H3K36 is larger in the 3’ region of genes and important for deAcetylation • Ubiquitylation of H2B is throughout the gene and permits H3K4 and H3K79 Methylation • H3K4 involves with positioning of Ist1 and has to do with proper poly-Adenylation and termination • H3K9 Methylation is observed in active genes thought its reason is not yet clear Have a nice Post-snow day!