* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Variation and the Monohybrid Cross
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
The Selfish Gene wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
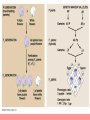
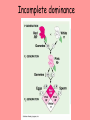
Variation and the Monohybrid Cross Higher Biology Significance of meiosis Allele: gene different forms of the same ‘Meiosis provides the opportunity for new combinations of the existing alleles of genes to arise” Independent assortment of chromosomes • Homologous pairs line up at equator during first meiotic division • Final position of any one pair is random relative to any other • Second meiotic division brings about independent assortment of chromosomes • This may lead to new phenotypes in the next generation Crossing over and separation of linked genes • Chromosome is aligned with its homologous partner during first meiotic division • Portions of chromatid exchanged at points called chiasmata Chiasmata • Chromatids become broken • Broken end of one joins with that of another • Alleles of linked genes can become separated • Formation of new allele combinations • Formation of new phenotypes Importance of Variation • Helps species adapt to a changing environment • ‘Survival of the fittest’ then occurs as a result of natural selection Monohybrid Cross • Cross between true-breeding parents with different alleles of the same gene • Genotype: gene • Phenotype: the alleles the individual possesses of a particular physical appearance of an individual Mendel’s First Law • The principle of segregation • alleles of a gene exist in pairs • when gametes form – members of each pair pass into different gametes – each gamete contains only one allele of each gene Incomplete dominance This powerpoint was kindly donated to www.worldofteaching.com http://www.worldofteaching.com is home to over a thousand powerpoints submitted by teachers. This is a completely free site and requires no registration. Please visit and I hope it will help in your teaching.