* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid tertiary structure wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
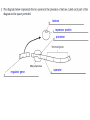
A regulator gene is a prokaryotic gene that codes for the production of a repressor protein An operator is a DNA segment that controls transcription by blocking RNA polymerase with a repressor protein; it is part of the operon. An intron is a section of a gene that is transcribed but not translated. An exon is a section of a gene that is transcribed and translated. A transcription factor is a protein that facilitates gene transcription by binding to RNA polymerase and to an enhancer. C D A B D A series of genes whose transcription is controlled by a single promoter and operator. Lactose bonds to the repressor protein, releasing it from the operator. This allows the lactase genes to be transcribed and translated. In the absence of lactose, the repressor protein binds to the operator, preventing transcription of the lactase genes. Without a nuclear envelope, there is no structure to separate newly synthesized RNA from ribosomes. Therefore, ribosomes can begin to translate the RNA as soon as it is formed, before it has had a chance to be modified. lactose repressor protein promoter regulator gene operator If the regulator gene were deleted then the repressor protein could no longer be produced. Without a repressor protein at the operator site, RNA polymerase would transcribe genes continuously. Transcription is activated because the lactose molecule has bound to the repressor protein. This causes the repressor protein to release from the operator site, which then permits RNA polymerase to transcribe the structural genes.