* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download E co
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
Synthetic biology wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
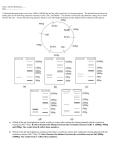
(a)The use of linkers to create tailor-made ends on cloning fragments.Synthetic oligonucleotide duplexes whose sequences represent EcoRI restriction sites are blunt-end ligated to a DNA molecule using T4DNA ligase.Note that the ligation reaction can add multiple linkers on each end of the blunt-ended DNA. EcoRI digestion removes all but the terminal one,leaving the desired 5’-overhangs.(b)cloning vectors often have polylinkers consisting of a multiple array of restriction sites at their coning sites, so restriction fragments generated by a variety of endonucleases can by incorporated into the vector.Nore that the polylinker is engineered not only to have multiple restriction sites bur also to have an uninterrupted sequence of codons,so this region of the vector has the potential for translation into protein.The sequence shown is the coning site for the vectors M13mp7 and pUC7;the colored amino acid residues are contiguous with the coding sequence of the lacZgene carried by this vector(see Figure 13.18)