* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Structure and Function Chapter 7
Survey
Document related concepts
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
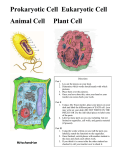
Cell Structure and Function Chapter 7 Cells are very diverse. What different kinds of cells do you have in your body? Name 5 kinds. ________________________ ________________________ ________________________ ________________________ ________________________ Even though cells are very different in function and appearance, all cells have certain features in common. All cells have a _________membrane. What are its 3 functions? ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ All cells use ________as a hereditary blueprint. Where is this material found? All cells contain __________________, all of the material inside the cell membrane except the nucleus. All cells must acquire and expend _________________. In prokaryotes…___________________________________ In eukaryotes…____________________________________ Where do green plants get their energy? _____________________________________________ Where do plant-eating animals (herbivores) get their energy? _____________________________________________ 1 Where do animals that eat other animals (carnivores) get their energy? _____________________________________________ What is the ultimate source (either directly or indirectly) of all energy for plants and animals? ____________________________________________ What would happen to life on Earth if the sunlight were blocked from the earth’s surface? ____________________________________________ All cells are small in size. The first cells were not seen until the late __________ when early microscopes were developed. Why are organisms made of many small cells and not one big cell? …because cells depend on the process of ____________ to move many substances through the cell and in and out of the cell. Diffusion is very ______________. Eukaryotic cells all have similar features The control center of the cell is called the ____________. It is enclosed by a double membrane called the ___________ __________________. Openings in the nuclear envelope called __________ allow for movement of substances in and out of the nucleus. 2 Structures inside the nucleus that contain DNA and proteins are called _____________________. Since DNA cannot leave the nucleus, genetic information is copied into molecules of __________ and sent out into the cytoplasm. This information is used to manufacture ________________. Name 5 ways plants can use large central vacuoles. _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ What cell organelles are known as “powerhouses of the cell”? _______________________ What is the function of these organelles? _________________________________________________ In what kinds of cells would you expect to find large numbers of these organelles? _____________________________________ In the space below label the picture of this organelle. Label the following in the diagram: outer membrane, inner membrane, cristae, matrix, intermembrane compartment. 3 An organelle that is responsible for photosynthesis is the _______________________. In what organisms is this organelle found? _________________________________________________ In the space below draw a picture of a chloroplast. Label these structures in your diagram: outer membrane, inner membrane, stroma, thylakoid, granum (stack of thylakoids). 4