* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Product Life Cycle
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
Brand ambassador wikipedia , lookup
Consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Grey market wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Planned obsolescence wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
Supermarket wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Product lifecycle wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Product placement wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Predictive engineering analytics wikipedia , lookup
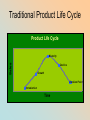
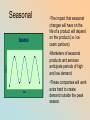
Introduction Growth Product Life Cycle Decision Point Decline Maturity Traditional Product Life Cycle Product Life Cycle Sales M aturity Decline Growth Decision Point Introduction Time Traditional PLC Introduction – When a new product is launched into the marketplace…the birth of a new product – Very expensive (warehouse space, new packaging, labeling, production equipment, market research costs etc.) – Marketing efforts are focused on selling to the early adopters (first consumers) – Will use either a PUSH strategy (efforts are focused on product placement in stores) or PULL strategy (use advertising to forge a +ve association with the product in the consumers mind) Growth • Word of mouth advertising is crucial at this stage, product must be visible • Companies will advertise heavily at this stage • The product will either catch on or fail Maturity • Sales of a product increase much slower • Marketers keep the name of their brand visible • Invest little $ in new advertising, while original promotional mix is less frequent • More chance for profitability because costs are low Decline • Happens when a company is unable to find new customers for their product(s) • Marketers will try various tactics to get out of this stage (re-design/re-package/reprice) Decision Point Stage • Marketers make important brand management decisions regarding the products future • Usually involves new promo and new pricing (example: Cow Brand baking soda made a market shift to focus on a product that removes odors from freezers, litter boxes etc.) Nontraditional PLC’s FAD •A product, service or idea that is extremely popular for a very brief period of time •Becomes unpopular just as quickly, vanishing soon after it’s introduction to the marketplace •When fads die, businesses run the risk of being caught with large amounts of unwanted inventory NICHE Sales Niche Time •A small section of the market that a product dominates •Because the market is so small, there is little competition •Example: the Pet Hotel in Peterborough, Ontario is a niche market because there are not enough consumers to make the market attractive to competitors, however the market is large enough to be profitable. Seasonal Seasonal •The impact that seasonal changes will have on the life of a product will depend on the product (I.e. Ice ceam parlours) Sales •Marketers of seasonal products and services anticipate periods of high and low demand Time •These companies will work extra hard to create demand outside the peak season.