* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plants
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
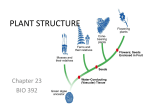
Describe four challenges to plants living on land and how the plants have adapted • How to Get Nutrients from land and air? Shoots (stems and leaves) and roots. • Staying “afloat” in air? Strong support tissue, lignin Describe four challenges to plants living on land and how the plants have adapted. • Retaining moisture. Waxy cuticle and stomata (pores) surrounded by guard cells • Reproducing in air – internal fertilization and embryo development. Seeds enclosed in protective “jackets” Pollen so sperm won’t dry out Identify the four major groups of plants and their major characteristics. Describe the characteristics of a pteridophyte, and give three examples of these plants. • Vascular plants(have xylem and phloem) that do not produce seeds, they reproduce by spores • Ferns, horsetails, club mosses What three structures do all vascular plants have? • Roots • Stems • Leaves List the four main groups of gymnosperms. • Ginkos • Cycads • Conifers • Gnetophytes What does a “naked” seed mean? • Not enclosed in an ovary Describe 2 unique features of angiosperms and how these features help the plants. • Flowers – attract pollinators • Fruit – protection of seeds, nutrition of seeds, helps with dispersal Characterize the two largest evolutionary branches of angiosperms. Describe their differences. Monocot • Single cotyledon • Parallel veins in leaves Dicot • Double cotyledon • Veined leaves Describe ways that humans depend on angiosperms. Name one way you utilized an angiosperm today. • • • • • Food Animal Food Clothing Fuel Ornamental Define “Fruit” • Ripened ovary of a flower Relate the structures of a flower to their reproductive functions, and indicate whether the structure is male, female, or neither. Describe root and shoot structures and functions • Vascular tissue, transport of nutrients and wastes, photosynthesis. What are the two functions of vascular tissue? • Transport • Structural support Describe three main plant tissues systems • Dermal Tissue: Outer covering or “skin” of the plant • Vascular Tissue: transports water, mineral nutrients, and organic molecules between roots and shoots (ex. xylem and phloem) • Ground Tissue: tissue inbetween dermal and vascular tissue that functions in photosynthesis, storage and support. Describe the two types of vascular tissue and their specific functions Xylem • Transports water and dissolved minerals up Phloem • Transports food from leaves to parts of plants that photosynthesize Trace the path of nitrogen from the atmosphere to a plant’s roots Explain how water loss from a plant is regulated Waxy cuticle Stomata = microscopic pores found on the under side of leaves that open and close Stomata Closed Stomata Open