* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plants Study Guide
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
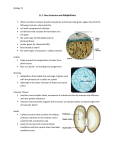
Plants Study Guide 1. Plants are multicellular, which means they have 2 or more cells. They are also eukaryotic which means they have a nucleus. They are also autotrophs (producers) which means they make their own food. 2. If plants have a system of tubes for transportation they are called vascular plants. If they lack these tubes they are called nonvascular plants. 3. Vascular tissue includes phloem which transports food and xylem which transports water and minerals. 4. Plants have two stages of their life cycle –the sporophyte and gametophyte. The sporophyte stage is when they produce spores. The gametophyte stage is when they produce gametes (sex cells/sperm and egg). 5. List 3 the methods of seed dispersal: a. wind b. water c. other organisms 6. What are cotyledons? seed leaves 7. What type of vascular plant produces “naked seeds”? gymnosperms 8. What type of vascular plant produces fruit? angiosperms 9. Monocots have one cotyledon and dicots have two cotyledons. 10. Parts of a Flower: 11. Define sepals: small leaf-like part of the flower that protects the developing petals 12. Why is the stigma sticky? pollen attaches to the stigma 13. After fertilization, what happens to the ovary in the diagram? (pg. 278) It develops into a fruit. 14. Germination is when the plant is pushing out of the seed. This occurs when the seed absorbs water. 15. What is the difference between the stomata and the cuticle? stomata—small opening on the underside of leaves where gases are exchanged; cuticle—waxy layer on leaves that helps retain water 16. What are root hairs used for? increase surface area of roots to help absorb more water and minerals 17. Define dormancy period of time when growth of a plant stops 18. Define tropism plants growth response towards or away from a stimulus 19. This is an ancestor to plants algae.