* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download A Tour of Cell Biology
Survey
Document related concepts
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
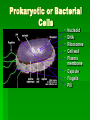
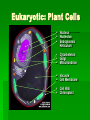
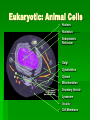
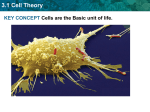
A Tour of Cell Biology Presented by Mary Markowski Today’s Goals! Introduction to cell biology To be introduced to the differences between bacterial, animal and plant cells Gain the ability to identify characteristics of all three types of cells Introduction to Living Cell Types Living cells divided into two types - prokaryotic and eukaryotic Division based on internal complexity Prokaryotic: Pre-nucleus Simple Small No compartmentalization Eukaryotic: true nucleus Complex Larger Highly compartmentalized The common feature that links all cells is the production of PROTEINS These are required for the growth, development and maintenance of all cells Prokaryotic or Bacterial Cells • • • • • Nucleoid DNA Ribosomes Cell wall Plasma membrane • Capsule • Flagella • Pili Cool Bacterial Growth Video! E Coli Movie Eukaryotic: Plant Cells Nucleus Nucleolus Endoplasmic Reticulum Cytoskeleton Golgi Mitochondrion Vacuole Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chloroplast Eukaryotic: Animal Cells Nucleus Nucleolus Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Cytoskeleton Cytosol Mitochondrion Secretory Vesicle Lysosome Vacuole Cell Membrane The Cell: A Busy Factory •Copyright 1996 Shawn GlynnA cell can be thought of as a "factory," with different departments each performing specialized tasks. Universal Organelles For both prokaryotic and eukaryotic Nucleoid or Nucleus with DNA Cell membrane Ribosomes Cytosol For animal and plant cells only (eukaryotic) All but cell wall and chloroplasts Only in plant cells, why? Structure and photosynthesis Implications / Significance Differences between the cells allow all of us to have specialized function Bacteria: invade and multiply rapidly! Plants: strength and photosynthesis Humans: the most complex multicellular organisms on earth! Conclusion 2 very distinct classes of cells Prokaryotic Bacteria Eukaryotic Plant Animal Fun Cell Quiz! We never knew cells could be so interesting! Works Cited Excel evaluation of websites