* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell
Survey
Document related concepts
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
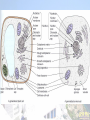
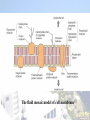
Chapter 2 Structure and functions Of the Cell Nucleus: For storage of genetic information. Rough Endoplasmic reticulum (rough ER) For protein synthesis Smooth Endoplasmic reticulum (smooth ER) For intra-cellular transport Golgi apparatus Related to secretory function Mitochondrion For aerobic respiration mitochondria (pl) Chloroplast For photosynthesis Lysosome For intra-cellular digestion The fluid mosaic model of cell membrane ATPase is an example of enzyme. Recognition protein to distinguish foreign molecules from self molecules. Receptor protein to recognize a signal (e.g. hormone) and then starts a specific biochemical reaction. Microvilli and pseudopodia These are the extensions of the cell membrane. Microvilli are common along the surface of absorptive cell. They increase the surface area for absorption. Pseudopodia are outgrowth from phagocytic cell to enclose and swallow the foreign materials. Nucleus: Contains chromatins which carry DNA. DNA consists of a number of genes. Genes produce mRNA which controls the ribosome to synthesize specific polypeptide/ protein. mRNA leaves the nucleus through the nuclear pores. Nucleolus (Nucleoli pl.) To produce ribosomal RNA which is the structural material of ribosome. In other words, nucleoli produce rRNA which is to build up ribosome. Ribosome is the site to carry out protein synthesis. Protein synthesis is based on the information of mRNA. The information of mRNA is copied from the DNA of the nucleus. Endoplasmic reticulum: Two types: Rough ER and Smooth ER Rough ER connects the external nuclear membrane. Both are for intra-cellular transport and act as cytoplasmic skeleton. Rough ER is for protein synthesis. Smooth ER is the site where lipids and steroids are made. Golgi apparatus: Protein synthesized by rough ER is transported to Golgi apparatus for storage, processing and modification into different forms such as enzymes, hormones. Golgi apparatus is related to secretion. Lysosome: Lysozome is originated from Golgi apparatus. It encloses hydrolytic enzymes called lysozymes. Functions: For break down of aged or worn out organelles. Acts as “suicide bag” to destroy the whole cell. For phagocytic cell, lysosome is for intra-cellular digestion of foreign materials e.g. pathogens, aged red blood cells. Mitochondrion It is bounded by double membranes. The inner membrane has many infolds called cristae to increase the surface area for attachment of enzymes and coenzymes. crista Aerobic respiration consists of three main stages, namely glycolysis, Krebs cycle and oxidative matrix phosphorylation. Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasmic matrix. The other two stages take place at the cristae and the matrix of the mitochondrion. Anaerobic respiration consists of glycolysis which takes place in the cytoplasmic matrix. Therefore no mitochondrion is needed. Vacuole and tonoplast Tonoplast is the internal boundary of vacuole. Vacuole contains cell sap which gives the turgidity to the cell and for storage of materials. Cilium and flagellum (Pl. forms: cilia and flagella) Cilium is short and numerous. Flagellum is long and few. They have the same internal structure. Each has two central microtubules and 9 peripheral microtubules. It gives a (9+2) pattern. These microtubules are contratile, giving the beating movement of cilium or flagellum. Cell wall, middle lamella (5), pit and plasmodesmata (2) Thin Cell wall is composed of cellulose with pectin. In addition, lignin or suberin is present in thick cell wall. E.g. xylem Middle lamella is a cementing layer between the cell wall of two adjacent cells. Some plant cells have pit for communication with the adjacent cells. Plasmodesma (plasmodesmata pl.) is the cytoplasm present along the pit. It can stream from one cell to another. Eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells Eucaryotic cell has membrane bounded nucleus and other organelles such as mitochondria. The membrane bounded organelles provide compartmentation to give specific conditions for the various biochemical reactions. Prokaryotic cell: Bacterial cells and blue green algae are of this type. The DNA is not bounded by nuclear envelop. It does not have other membrane bounded organelles.