* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CH3- part2
Survey
Document related concepts
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
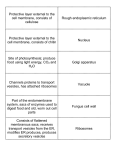
“little organs” Membrane bound structures within the cytoplasm that have specialized functions. Include: Organelles Mitochondria One of largest organelles Called “__________ of the cell” ◦ produces 95% of the cell’s energy (ATP) Active cells have higher energy demands and therefore more mitochondria. Can divide through ____________ -or the pinching of itself in half when the cells energy requirements increase. Tend to be elliptical or round with an outer smooth membrane and inner involuted membrane. Inner membrane forms ____________ ,which increase internal working area and the _________ (enzyme-rich liquid housed in mitochondria that is used for metabolism). Cristae are site of ATP production The more active the mitochondria, the more cristae it has. Mitochondria Most numerous organelle in the cell. Made of two glubular subunits composed of _________ and ____ that fit together. Site of _____________ synthesis. ◦ assemble amino acids into chains instructed by the cell’s DNA May be attached to the endoplasmic reticulum (rough ER) or free in the cytoplasm Affects the destination of the protein. Ribosomes Series of flattened tubes stacked on one another and bent into a crescent shape. Walls are made of a lipid bilayer and are continuous with the membrane of the nucleus. ◦ Rough ER is covered in ribosomes is involved in production of ____________, which then move into the ER (cisternae) where they are modified before going to the Golgi apparatus. ◦ Smooth ER is connected to Rough ER and is active in synthesis and storage of __________. Lacks ribosomes. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Modification, packaging, and distribution center Found near _________ and is similar in structure to ER. ◦ stacks of flattened, crescent shaped cisternae Receives and modifies proteins produced by ER that is sent in sacs. ◦ sacs fuse with the Golgi apparatus and release proteins into its cisternae Once modification is completed, they are packaged in __________ and travel out into the cell. Golgi Apparatus Specialized vesicle formed by Golgi apparatus. Contain ____________ ____________. Membrane fuses with engulfed bacteria or cell nutrients and digests them. Considered “__________ of the cell”. When cells die, lysosomes within burst open and enzymes are released into the cytosol. ◦ Enzymes digest organelles and nucleus of the cell (____________). Lysosomes Membranous sacs containing enzymes that are found throughout the cell. Do not develop from Golgi. Instead come from peroxisomes pinching in half. ◦ Remove _______ __________, normal products of cellular metabolism but can be harmful in large numbers (interfere with protein, lipid, and nucleic acid structures). 2 major enzymes used: ◦ _________________-assist in conversion in free radicals to hydrogen peroxide. ◦ _________________-reduce hydrogen peroxide to water. Peroxisomes