* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
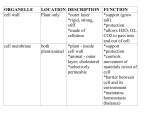
Download Protective layer external to the cell membrane, consists of cellulose
Survey
Document related concepts
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
Protective layer external to the cell membrane, consists of cellulose Rough endoplasmic reticulum Protective layer external to the cell membrane, consists of chitin Nucleus Site of photosynthesis; produce food using light energy, CO2 and H2O Golgi apparatus Channels proteins to transport vesicles, has attached ribosomes Vacuole Part of the endomembrane system, sacs of enzymes used to digest food and old, worn out cell parts Fungus cell wall Consists of flattened membranous sacs; receives transport vesicles from the ER, modifies ER produces, produces secretory vesicles Ribosomes Forms the boundary of the cell, acts as a selective barrier allowing certain materials to pass but not others Chromatin Contains most of the genes that control the eukaryotic cell, contains the nucleolus and chromatin Lysosome Where the components of the ribosome are synthesized and assembled; found in the nucleus Mitochondria Consists of DNA and protein, condenses to form chromosomes Transport vesicle Double membrane that forms the boundary between the nuclear contents and the cytoplasm; perforated with pores Plant cell wall Site of protein synthesis; suspended in the cytosol or attached to the ER Cell membrane Carries ER products to the Golgi Chloroplast Membrane bound sacs, larger than vesicles, stores water and dissolved nutrients Cytoskeleton Site of cellular respiration, produces ATP from sugar Nuclear membrane Supports the shape of the cell, anchors organelles and serves as a “track” for organelles to move on. Extra cellular matrix Proteins found outside an animal cell that function in support, adhesion and movement Nucleolus