* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant & Animal Cells
Survey
Document related concepts
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
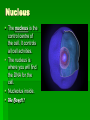
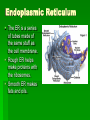
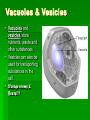
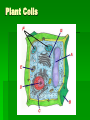
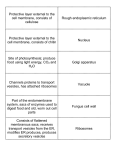
Plant & Animal Cells The Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke in 1663 looked at plant cells under a microscope and thought they looked like the cells monks lived in within their monasteries. As our microscopes became more powerful over the years, we have learned a great deal more about the inner workings of the cell. Cell Theory The cell theory outlines the importance of cell to living things. 1. Cells are the basic structures that make up living things. 2. Cells dictate the function of living things. 3. All cells come from preexisting cells. The average human body contains between 10-100 trillion cells. 100,000,000,000,000 cells!!! Cell Organelles A cell is like our body in that it has a number of parts that must all work together in order for the cell to function properly. These little parts within the cell are called organelles (little organs). Organelles look after a number of jobs within the cell such as… Intake of nutrients Movement Growth Responsiveness Gas exchange Waste excretion Reproduction Cell Membrane The cell membrane is a protective barrier around the cell. It controls what goes into or out of the cell. Security!!! Cytoplasm The cytoplasm is a jelly-like substance that fills the cell and surrounds the organelles. It contains the nutrients that the cell needs to survive. The Work Place!!! Nucleus The nucleus is the control centre of the cell. It controls all cell actvities. The nucleus is where you will find the DNA for the cell. Nucleolus inside. The Boss!!! Mitochondria The mitochondria produce energy for the cell. Cellular Respiration Sugar ATP!!! Powerhouses!!! Ribosomes Ribosomes are the tiny protein builders within the cell. Proteins are the “working molecules” of the body. Workers!!! Golgi Apparatus The Golgi apparatus modifies, sorts and packages proteins for delivery within or out of the cell. The Golgi makes vesicles for transport. Shipping & Receiving!!! Endoplasmic Reticulum The ER is a series of tubes made of the same stuff as the cell membrane. Rough ER helps make proteins with the ribosomes. Smooth ER makes fats and oils. Vacuoles & Vesicles Vacuoles and vesicles store nutrients, waste and other substances. Vesicles can also be used for transporting substances in the cell. Storage rooms & Boxes!!! Lysosomes Lysosomes digest materials in the cell using enzymes. The breakdown invaders and old parts of the cell. Bouncers & Recyclers!!! Cytoskeleton The cytoskeleton is made of protein filaments and helps the cell maintain its shape. Structure equals Function!!! Iron Girders!!! Cell Wall The cell wall is only in plant cells and it is a rigid frame that provides strength, protection and support. The Great Wall!!! Chloroplasts The chloroplast is only in plants and it carries out the process of photosynthesis. They make glucose…sugar!!! Solar Panels!!! Animal Cells Plant Cells Who has both plant and animal cells???