* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Cell
Survey
Document related concepts
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
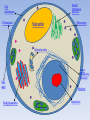
Plant Cell NOLAN ADAIR PERIOD 5 Mrs. Beaman: E-Core Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Cell membrane Chloroplast Vacuole Ribosomes Mitochondria Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Cell wall Golgi Apparatus Nucleus Nucleolus Vacuole • Vacuoles tend to be large in plant cells and play several roles: 1. Storing nutrients and waste products 2. Helping increase cell size during growth 3. Acting much like lysosomes of animal cells 4. Regulates turgor pressure in the cell Ribosomes • Ribosomes are packets of RNA and protein that play a crucial role in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells • Site of protein synthesis • Each ribosome consists of two parts – a large and a small subunit Nucleus • The most obvious organelle in any eukaryotic cell • Enclosed in a double membrane and communicates with the surrounding cytosol • Within the nucleus is the DNA responsible for providing the cell with its unique characteristics Nucleolus • The prominent structure in the nucleus is the nucleolus • The nucleolus produces Ribosomes Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum • It is called this because it appears smooth by electron microscopy • Plays different functions depending on the specific cell type including lipid and steroid hormone synthesis • Breakdown of lipid – soluble toxins in liver cells • Control of calcium release in muscle cell contraction Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum • Appears ‘pebbled’ by electron microscopy due to the presence of numerous Ribosomes on its surface • Proteins synthesized on these Ribosomes collect in the endoplasmic reticulum for transport throughout the cell Chloroplast • Specialized organelles found in all higher plant cells • Contain the plant cell’s chlorophyll responsible for the plant’s green color • Have a double outer membrane Golgi Apparatus • Is a membrane – bound structure with a single membrane • Is actually a stack of membrane – bound vesicles that are important in packaging macromolecules for transport elsewhere in the cell • Stack of larger vesicles is surrounded by numerous smaller vesicles containing those packaged macromolecules Cell Membrane • Every cell is enclosed in a membrane • Exposed heads of the bilayer are hydrophilic, meaning that they are combatable with water both within the cytosol and outside of the cell • Is made more complex by the presence of numerous proteins that are crucial to cell activity Cell Wall • Plant cells have a rigid, protective cell wall made up of polysaccharides • The cell wall provides and maintains the shape of these cells and serves as a protective barrier • Fluid collects in the plant cell vacuole and pushes out against the cell wall Mitochondrion • Provides the energy a cell needs to move, divide, produce secretory products • They are the power centers of the cell • Are membrane – bound organelles • Have a double membrane • About the size of bacteria, but may have different shapes depending on the cell types