* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Neurotransmitters
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
Vesicular monoamine transporter wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Eating disorder wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Biology of depression wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
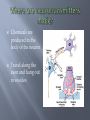
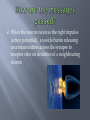
Psych 11 Kabotoff chemicals which transport information across the synaptic cleft between neurons They send many different types of messages: signal to relax a muscle - chemical reward for engaging in a particular task Serotonin Dopamine GABA Glutamate Opiate Noradrenaline Endocannabinoid Acetylcholine Sleep, arousal levels, emotion Higher levels of serotonin activate hypothalamus and frontal cortex 1999 Buddhist monks dep f n w, cold temp, 48hrs=hallucinations Too low=sleep or eating disorders, depression Too high =OCD Linked to creating memory (stim hippocampus) and muscle contraction Affected in Alzheimer’s patients Too low = paralysis Voluntary movement, learning, feelings of pleasure Tied to depression and vital to chemical dependency treatment Black out or binge drinkers seek the feeling of numbness when they use alcohol in excess Too much=psychotic, hallucinations Too little=clinically depressed Calms things down, too low=seizures Counteracts glutamate and other stimulant neurotransmitters Genetic predisposition – people who talk fast, worry, get fired up etc have a LOT of this .. Huntington’s disease decreases this, causes tremors, personality changes Mood, alertness, quick response (sex, eating, thirst) Too high=high blood pressure, nervous, anxiety Too low=lethargy, lack of motivation, depression Creates euphoric feeling i.e. endorphins Is addictive Prescription: Morphine, Vicodin, OxyContin, Dilaudid, Demerol, Codeine But can also cause pain if taken over a long period of time Chemicals are produced in the body of the neuron Travel along the axon and hang out in vesicles When the neuron receives the right impulse (action potential) , a vesicle bursts releasing neurotransmitters across the synapse to receptor sites on dendrites of a neighbouring neuron Neurotransmitters are the most important molecule in nearly every living thing Can be excitatory or inhibitors Some Factors affecting the release of neurotransmitters: genetics eating habits exposure to chemical substances stress conditions such as attention deficit disorder, autism, and other genetically linked disorders commonly present with imbalances in the level of neurotransmitters released by certain neurons Lack of protein in the diet, results in an absence in the amino acids needed to produce neurotransmitters for later release diets low in omega-3 and other fatty acids Synthetic chemicals also affect the release of neurotransmitters, either intentionally or unintentionally (drugs vs chem weapons)