* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Notes - The Nervous System
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
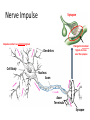
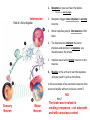
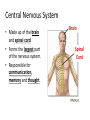
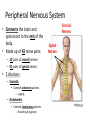
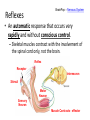
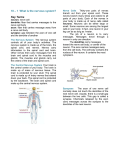
The Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System • The nervous system is the body’s command system. – Receives information about what is happening both inside and outside your body. – Stimuli – Directs that way in which your body needs to respond to this information. – Response – Helps the body to maintain homeostasis. Organization of the Nervous System • Made up of nervous tissue • Has two divisions: – Central nervous system (CNS) – Peripheral nervous system (PNS) • Main organs: – Brain – Spinal cord – Sensory organs; eyes, ears, nose, tongue, and skin Nervous Tissue • Made up of cells called Neurons, nerve cell. – Carry information through your nervous system. Dendrites Cell Body Nucleus Axon Axon Terminals Synapse Characteristics of a Neuron • Parts of the Neuron: – Dendrites • Carry impulses toward the cell body – Cell body • Contains the nucleus • Controls all the activities of the cell – Axon Nerve Fibers – a bundle of nerve fibers – nerve. • Carry impulses away from the cell body – Axon Terminal • Ends of an axon • Pass a message on to the neighboring neuron’s dendrites – Synapse • Space separating the axon terminal of one neuron and the dendrites of the neighboring neurons. Path of a Nerve Impulse • Nerve Impulse – the message being carried throughout the body by nerves. – ONLY travel in one direction – Travel as fast as 120 m/sec • Carried as both electrical and chemical messages – Messages come in from different stimuli and trigger electrical impulses. – At the end of the axon it is changed into a chemical message so it can cross over the synapse – neurotransmitters. Nerve Impulse Synapse Impulses come in as electrical signals Changed to chemical Signals to cross over the synapse Dendrites Cell Body Nucleus Axon Axon Terminals Synapse Types of Neurons 1. Sensory Neuron – picks up stimuli from the internal and external environments. – Location where the stimuli is received - Receptor. • Eyes, ears, nose, mouth, skin 2. Interneurons – carry nerve impulses from one neuron to another. – The brain and spinal cord interpret messages and determine appropriate reactions. 3. Motor Neuron – Send an impulse to the muscle resulting in a response to the stimuli. – Muscle tissue responds by contracting – Effector 1. Receptors in your ear hear the phone. – Interneuron The ear is a sensory organ. 2. Receptors trigger nerve impulses in sensory neurons. 3. Nerve impulses pass to interneurons in the brain. 4. The interneurons interpret the nerve impulses and decide on a response, you should answer the phone. 5. Impulses travel along motor neurons to the muscles. 6. Muscles in the arm carry out the response and you reach to pick up the phone. Is this an example of an automatic response that occurred rapidly without conscious control? NO Why? Sensory Neuron Motor Neuron The brain was involved in creating a response – not automatic and with conscious control Central Nervous System • Made up of the brain and spinal cord. • Forms the largest part of the nervous system. • Responsible for communication, memory and thought. Brain Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System • Connects the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body. • Made up of 43 nerve pairs: – 12 pairs of cranial nerves – 31 pairs of spinal nerves • 2 divisions: – Somatic • Controls voluntary actions – jogging – Autonomic • Controls involuntary actions – Breathing & digestion Cranial Nerves Spinal Nerves BrainPop – Nervous System Reflexes • An automatic response that occurs very rapidly and without conscious control. – Skeletal muscles contract with the involvement of the spinal cord only, not the brain. Reflex Receptor Interneuron Stimuli Motor Neuron Sensory Neuron Muscle Contracts - effector