* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Primary Structure of Proteins
Survey
Document related concepts
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Structural alignment wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
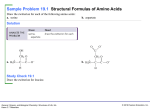
19.4 Protein Structure: Primary and Secondary Levels The secondary structure of a protein describes the structure that forms when amino acids form hydrogen bonds between the atoms in the backbone and atoms on the same or another peptide chain. The secondary structure in silk is a β-pleated sheet. Learning Goal Describe the primary and secondary structures of a protein. General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Primary Structure of Proteins A protein is a polypeptide of 50 or more amino acids with biological activity. The primary structure of a protein is the particular sequence of amino acids held together by peptide bonds. Ala–Leu–Cys–Met General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Primary Structure A thyroid hormone that stimulates the release of thyroxin is a tripeptide with the amino acid sequence Glu–His–Pro, EHP. Although other amino acid sequences of these three amino acids are possible, only the specific sequence or primary structure of Glu−His−Pro produces hormonal activity. General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Primary Structure of Insulin Insulin • was the first protein to have its primary structure determined. • has a primary structure of two polypeptide chains linked by disulfide bonds. • has a chain A with 21 amino acids and a chain B with 30 amino acids. General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Study Check Answer the questions for the following tripeptide: A. What is the N-terminus? B. What is the C-terminus? C. What is the name of the tripeptide? General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Study Check Answer the questions for the following tripeptide: A. What is the N-terminus? Phe B. What is the C-terminus? Ala C. What is the name of the tripeptide? phenylalanylcystylalanine General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Study Check Write the names and three-letter abbreviations of the tripeptides that could form from two glycines and one alanine. General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Solution Write the names and three-letter abbreviations of the tripeptides that could form from two glycines and one alanine. Glycylglycylalanine Gly–Gly–Ala Glycylalanylglycine Gly–Ala–Gly Alanylglycylglycine Ala–Gly–Gly General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc.