* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Catalytic triad wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Structural alignment wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
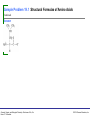
Sample Problem 19.1 Structural Formulas of Amino Acids Draw the zwitterion for each of the following amino acids: a. serine b. aspartate Solution a. b. Study Check 19.1 Draw the zwitterion for leucine. General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Sample Problem 19.1 Structural Formulas of Amino Acids Continued Answer General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Sample Problem 19.2 Classification of Amino Acids Using Table 19.2, indicate each of the following for the amino acid shown: a. b. c. d. name, three-letter, and one-letter abbreviations polar or nonpolar has a neutral, acidic, or basic R group interaction with water as hydrophobic or hydrophilic Solution a. phenylalanine, Phe, F c. neutral General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake b. nonpolar d. hydrophobic © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Sample Problem 19.2 Classification of Amino Acids Continued General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Sample Problem 19.2 Classification of Amino Acids Continued Study Check 19.2 Using Table 19.2, indicate each of the following for the amino acid shown: a. b. c. d. name, three-letter, and one-letter abbreviations polar or nonpolar has a neutral, acidic, or basic R group interaction with water as hydrophobic or hydrophilic Answer a. serine, Ser, S c. neutral General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake b. polar d. hydrophilic © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Sample Problem 19.3 Amino Acids in Acidic or Basic Solution The pI of glycine is 6.0. Draw the structural formula and state the overall charge for glycine at a. pH 6.0 and at b. pH 8.0. Solution a. At a pH of 6.0, glycine has an ammonium group and a carboxylate group, which give it an overall change of zero (0). b. At a pH of 8.0 (basic solution), the —NH3+ group loses H+ to become —NH2, which has no charge. Because the carboxylate group (—COO–) remains ionized, the overall charge of glycine at pH 8.0 is negative (1–). Study Check 19.3 Draw the structural formula for glycine at pH 3.0 and give the overall charge. General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Sample Problem 19.3 Amino Acids in Acidic or Basic Solution Continued Answer General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Sample Problem 19.4 Drawing a Peptide Draw the structure and give the name for the tripeptide Gly–Ser–Met. Solution Step 1 Draw the structures for each amino acid in the peptide, starting with the N-terminus. General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Sample Problem 19.4 Drawing a Peptide Continued Step 2 Remove the O atom from the carboxylate group of the N-terminus and two H atoms from the ammonium group in the adjacent amino acid. Repeat this process until the C-terminus is reached. General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Sample Problem 19.4 Drawing a Peptide Continued Step 3 Use peptide bonds to connect the amino acid residues. The tripeptide is named by replacing the last syllable of each amino acid name with yl, starting with the N-terminus. The C-terminus retains its complete amino acid name. N-terminus glycine is named glycyl serine is named seryl C-terminus methionine keeps its full name The tripeptide is named glycylserylmethionine. General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Sample Problem 19.4 Drawing a Peptide Continued Study Check 19.4 Draw the structure and give the name for Phe–Thr, a section in glucagon, which is a peptide hormone that increases blood glucose levels. Answer General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Sample Problem 19.5 Primary Structure What are the three-letter and one-letter abbreviations of the tetrapeptide that contains two valines, one proline, and one histidine if the N-terminus is histidine and the C-terminus is proline? Solution The tetrapeptide starts with the N-terminus, histidine, followed by two valine residues, and ends with the C-terminus, proline. Three-letter abbreviations: His–Val–Val–Pro One-letter abbreviations: HVVP Study Check 19.5 What are the three-letter and one-letter abbreviations of a tripeptide containing two glycines and one tyrosine, if the N-terminus is tyrosine? Answer Tyr–Gly–Gly (YGG) General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Sample Problem 19.6 Identifying Protein Structures Identify the secondary structure (α helix, β-pleated sheet, or triple helix) described in each of the following statements: a. a structure that has hydrogen bonds between adjacent polypeptide chains b. three helical polypeptides woven together c. a peptide chain with a coiled or corkscrew shape that is held in place by hydrogen bonds Solution a. β-pleated sheet b. triple helix c. α helix Study Check 19.6 Which attractive force holds secondary structures together in proteins? Answer hydrogen bonding General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Sample Problem 19.7 Interaction Between Residues in Tertiary Structures What type of interaction would you expect between the residues of each of the following amino acids in a tertiary structure of a protein? a. cysteine and cysteine b. glutamate and lysine c. tyrosine and water Solution a. Two cysteines, each containing —SH, will form a disulfide bond. b. The interaction of the —COO– in the residue of glutamate and the —NH3+ in the residue of lysine will form an ionic bond called a salt bridge. c. The residue in tyrosine has an —OH group that is attracted to water by hydrophilic interactions. Study Check 19.7 Would you expect to find valine and leucine on the outside or the inside of the tertiary structure? Why? Answer Both valine and leucine have nonpolar residues and would be found on the nonpolar inside of the tertiary structure. General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Sample Problem 19.8 Identifying Protein Structure Indicate whether the following interactions are responsible for primary, secondary, tertiary, or quaternary protein structures: a. disulfide bonds that form between portions of a protein chain b. peptide bonds that form a chain of amino acids c. hydrogen bonds between the H of a peptide bond and the O of a peptide bond four amino acids away Solution a. Disulfide bonds are a type of interaction between amino acid residues found in the tertiary and quaternary levels of protein structure. b. The peptide bonds in the sequence of amino acids form the primary level of protein structure. c. The hydrogen bonds between the peptide bonds along the polypeptide chain form the secondary structures of α helix or β-pleated sheet Study Check 19.8 What structural level is represented by the hydrophobic side chains of the amino acid residues at the center of a globular protein? Answer tertiary structure General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Sample Problem 19.9 Denaturation of Proteins Describe the denaturation process in each of the following: a. An appetizer known as ceviche is prepared without heat by placing slices of raw fish in a solution of lemon or lime juice. After 3 or 4 h, the fish appears to be “cooked.” b. When baking scalloped potatoes, the added milk curdles (forms solids). Solution a. The acids in lemon or lime juice break down the hydrogen bonds between polar residues and disrupt salt bridges, which denature the proteins of the fish. b. The heat during baking breaks apart hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic interactions between nonpolar residues in the milk proteins. When the milk denatures, the proteins become insoluble and form solids called curds. Study Check 19.9 Why is a dilute solution of AgNO3 used to disinfect the eyes of newborn infants? Answer The heavy metal Ag+ denatures the proteins in bacteria that cause gonorrhea. General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc.