* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SBI4U Translation
Synthetic biology wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid tertiary structure wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
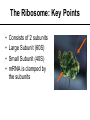
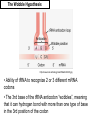
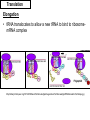
Protein Synthesis: Translation The Ribosome: Key Points • • • • Consists of 2 subunits Large Subunit (60S) Small Subunit (40S) mRNA is clamped by the subunits http://www-tc.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/photo51/images/pict-2001ribosome.jpg The Ribosome: Key Points • Ribosome moves toward the 3’ end of the mRNA (5’ to 3’) direction • Reads codons and adds amino acids to a growing polypeptide chain • Reading Frame – determines the sequence in which the codons are read 5’ 3’ CAUGCAUGGCAUC • This is what the ribosome sees • It reads the mRNA in codons in a 5’ to 3’ direction (the ribosome moves toward the 3’ end of the mRNA molecule) • There are three possible “phases” the codons can be read 5’ Here Here And here 3’ CAUGCAUGGCAUC • There are three possible phases the codons can be read • This can lead to three completely different sequences! • Thus it is vital that the mRNA is positioned correctly within the ribosome Why? Try This! • The following is the sequence of the coding DNA strand in a prokaryote • Determine the sequence of the transcribed mRNA • Then, using the Genetic Code on p240, determine the polypeptide chain • How do you know where to start? 5' GGGATCGATGCCCCTTAAAGAGTTTACATATTGCTGGAGGCGTTAACCCCGGA 3’ tRNA • Delivers the amino acids to the ribosome • How does a tRNA know when to join the ribosome? tRNA • The anticodons of some tRNAs recognize more than one codon • This is possible because the rules for base pairing between the third base of the codon and anticodon are relaxed (called the wobble hypothesis) – At the wobble position, U on the anticodon can bind with A or G in the third position of a codon • Why would this be beneficial? The Wobble Hypothesis http://www.mun.ca/biology/scarr/MGA2-03-30.jpg • Ability of tRNA to recognize 2 or 3 different mRNA codons • The 3rd base of the tRNA anticodon “wobbles”, meaning that it can hydrogen bond with more than one type of base in the 3rd position of the codon Elongation (refer to Fig 4 on p252) • After the start codon is recognized (AUG – methionine) the subsequent amino acids are added • The ribosome has two sites for tRNA – A site (acceptor) – P site (peptide) • The “charged” tRNA carrying the next amino acid in sequence enters the A site • Then the ribosome moves to the next codon and the “uncharged” tRNA is moved to the P site (the exception to this rule is the start tRNA with methionine that enters the P site directly) • A peptide bond forms between the amino acids and the uncharged tRNA is recycled back to the cytoplasm Translation Elongation • tRNA translocates to allow a new tRNA to bind to ribosomemRNA complex http://library.thinkquest.org/C0123260/basic%20knowledge/images/basic%20knowledge/RNA/translation%20steps.jpg Termination (refer to Fig 4 e & f on p252) • Once the stop codon (UGA, UAG, or UAA) is reached, the ribosome will come to a halt (there are no corresponding tRNA’s) • Then, a protein release factor comes in to aid the release of the polypeptide chain from the ribosome • Translation of the gene of interest ends • Alterations may occur – read p253 Homework • Read section 5.4 which starts on page 250 • On page 254, do questions #1-4,6-9,10