* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Astable multivibrator
Survey
Document related concepts
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Invention of the integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Molecular scale electronics wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Nanogenerator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Crossbar switch wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
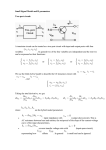
The Astable Multivibrator (a) Circuit diagram +6V +6V R3 R1 R2 C1 B2 T1 C2 R4 B1 T2 0 0 (b) Output voltages (Suggested values for the resistors: R1 = 6.8k, R2 = 6.8k, R3 = 2.2k, R4 = 2.2k) O1 O2 B1 B2 We will assume that transistor T1 is ON initially and transistor T2 is OFF. 1 When T1 is on O1 is at 0.2 V and B1 is at 0.7 V T2 is off and O2 is at 6 V and B2 is at –5.3 V C1 charges up through R1 and C2 charges up through R4 As soon as B2 reaches 0.7 V T2 switches on Note that C1 charges slowly through the large resistor R1 while C2 charges more quickly through the small resistor R4. When T2 switches on O2 drops to nearly 0 V, B1 drops by 6 V to –5.3 V and T1 goes off. Both sides of C2 will drop by 6 V and it will take some time for C2 to adjust its charge, the potential difference across it cannot change instantly. The cycle now repeats for the transistor. The charge discharge rate and hence the switching action of the circuit depends on C and R. 2