* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Structure Vocabulary
Survey
Document related concepts
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
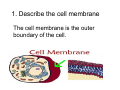
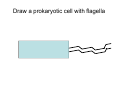
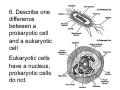
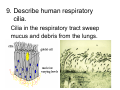
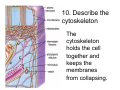
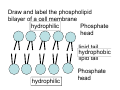
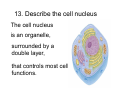
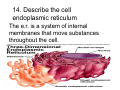
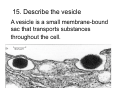
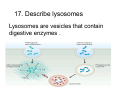
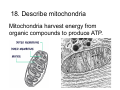
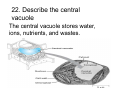
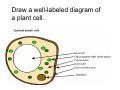
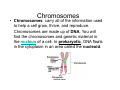
Cell Structure Vocabulary 1. Describe the cell membrane The cell membrane is the outer boundary of the cell. 2. Describe the cell’s cytoplasm The interior of the cell from the nuclear membrane to the cell membrane is the cytoplasm. 3. Describe the ribosome’s function Ribosomes are structures upon which proteins are made. 4. Describe the prokaryotic cell A prokaryotic cell lacks a nucleus and internal compartments (organelles). 5. Describe flagella Flagella are long threadlike structures that enable movement. Draw a prokaryotic cell with flagella 6. Describe one difference between a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus, prokaryotic cells do not. 7. Describe a cell organelle A cell organelle is a cell structure that carries out specific activities. 8. Describe a difference between cilia and flagella Cilia are short hairlike structures used for movement. Flagella are longer. Flagella= whip Cilia = eyelash 9. Describe human respiratory cilia. Cilia in the respiratory tract sweep mucus and debris from the lungs. 10. Describe the cytoskeleton The cytoskeleton holds the cell together and keeps the membranes from collapsing. Draw and label the phospholipid bilayer of a cell membrane hydrophilic Phosphate head lipid tail hydrophobic lipid tail hydrophilic Phosphate head 11. Describe the lipid bilayer The lipid bilayer is a double layer of hydrophilic phosphate head attached to a two hydrophobic phosphate tails. hydrophilic hydrophobic 12. List and tell the function of four types of cell membrane proteins 1. cell-surface proteins- identifies cell 2. receptor protein- binds to substances outside the cell 3. enzyme- assists chemical reactions 4. transport protein- helps substances move across the cell membrane 13. Describe the cell nucleus The cell nucleus is an organelle, surrounded by a double layer, that controls most cell functions. 14. Describe the cell endoplasmic reticulum The e.r. is a system of internal membranes that move substances throughout the cell. 15. Describe the vesicle A vesicle is a small membrane-bound sac that transports substances throughout the cell. 16. Describe the Golgi apparatus The Golgi apparatus are membranebound sacs that modify, package and send products of the e.r. 17. Describe lysosomes Lysosomes are vesicles that contain digestive enzymes . 18. Describe mitochondria Mitochondria harvest energy from organic compounds to produce ATP. 19. Describe why mitochondria need DNA Mitochondria need DNA to make some of their own proteins. 20. Describe the cell wall The cell wall is composed of proteins and carbohydrates. The c.w. supports and maintains the cell’s shape. 21. Describe the chloroplasts Chloroplasts use light energy to make carbohydrates. 22. Describe the central vacuole The central vacuole stores water, ions, nutrients, and wastes. Draw a well-labeled diagram of a plant cell. Chromosomes • Chromosomes carry all of the information used to help a cell grow, thrive, and reproduce. Chromosomes are made up of DNA. You will find the chromosomes and genetic material in the nucleus of a cell. In prokaryotic, DNA floats in the cytoplasm in an area called the nucleoid.