* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download LAYERS OF THE EARTH
Survey
Document related concepts
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
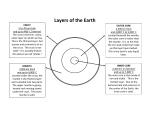
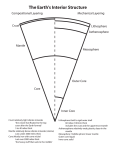
LAYERS OF THE EARTH 1. lithosphere – the rigid (hard) outer shell of the earth. It includes the crust and the top of the upper mantle. 2. crust – the outermost, solid layer of the earth. It is made up of land and ocean floor. It ranges in thickness from about 5 miles (oceanic crust) to 25 miles (continental crust). The crust is more dense under the ocean and less dense under the continents. The oceanic crust is mostly composed of basalt. The continental crust is mainly made of granite. The crust temperature is up to 930 degrees Farenheit. 3. asthenosphere – the layer of the upper mantle where rocks melt due to high temperatures (above 2,200 F). This layer is flowing, which allows the continents to drift. 4. mantle – the thick layer below the earth’s crust (about 1,800 miles thick). The lower mantle, or inner mantle, is solid. Mantle rock is constantly being driven up toward the surface by the enormous temperatures below, which cause huge convection currents. As mantle rock nears the surface, it cools and sinks back down. The temperature of the mantle goes up to about 5,000 F. 5. outer core – consists of metals in a fluid state. This is where Earth’s magnetic field is generated. The outer core is mainly iron and nickel and it is 1,400 miles thick. 6. inner core – The inner core is solid and is made of nickel and iron. The temperature of the inner core is about 7,000 F and it is about 800 miles thick.