* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Key - UCSB CLAS
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic resolution wikipedia , lookup
Chemical biology wikipedia , lookup
Lewis acid catalysis wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular biology wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Self-assembling peptide wikipedia , lookup
Acid dissociation constant wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
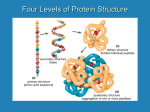
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Abiogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleophilic acyl substitution wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Acid–base reaction wikipedia , lookup
Acid strength wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
CLAS – Chem109C – Ch 22 – Key 1. Answer the following: a. Which amino acid(s) is achiral? glycine b. Are naturally occurring amino acids D or L? L 2. Draw the following amino acids at pH = 0, 5, and 13. a. Valine + O O + H3N OH H3N O O - O - pH = 13 pH = 5 pH = 0 H2N b. Glutamate + O O + H3N OH HO H3N O - O - O O H2N - O O O pH = 13 pH = 5 pH = 0 - O c. Lysine + H3N O + OH + H3N O O O - H2N O - + NH3 NH3 NH2 pH = 0 pH = 5 pH = 13 3. Calculate the pI of the following amino acids. 2.16+9.18 a. Phenylalanine ⇒ pI = = 5.67 b. Histidine ⇒ pI = c. Aspartic Acid ⇒ pI = 2 6.04+9.17 2 2.09+3.86 2 = 7.6 = 2.98 4. What is the net charge of the following amino acids at the designated pHs? 2.21+9.15 a. Serine at pH = 4 ⇒ pI = = 5.68 since the pH < pI there is a net positive 2 b. Arginine at pH = 9 ⇒ pI = c. Glutamic acid at pH = 5⇒ pI = 9.04+12.48 2 2.19+4.25 2 = 10.76 = 3.22 since the pH > pI there is a net negative since the pH > pI there is a net negative 5. Which amino acids are the most polar and nonpolar? Most polar amino acids have a charge on their side chain such as asp, glu, his, lys and arg. However the most nonpolar amino acids have a long saturated hydrocarbon as their side chain such as leu and ile. 6. Thin layer chromatography of a solution of threonine, valine, lysine, alanine and serine yielded the following; determine which amino acid goes with each spot? from top (most nonpolar to bottom (most polar) ⇒ val, ala, thr, ser, lys 7. Gel electrophoresis of a solution of histidine, tyrosine, lysine, aspartate and glutamic acid yielded the following determine which amino acid goes with each spot? anode cathode c a from left (most negative or lowest pI) to right (most positive or highest pI) 8. Show how valine can be synthesized via… a. HVZ O O 1. Br2, PBr3 OH 2. H2O O Br O 3. xs NH3 OH Br + NH3 Br O - b. Reductive amination O 1. xs NH3 O OH O O O 2. H2, Pd/C - + NH O - NH3 c. N-Phthalimidomalonic ester synthesis O O EtO OEt + OEt N O N EtO O O 4. H2O, HCl O OEt N 2. - OEt EtO O O O - C N 3. (CH3)2CHBr OEt O O EtO O O - Br O O O O + OH NH3 d. Strecker Sythesis 2. -CN, HCl 1. NH3, trace acid O NH N + NH3 2. H2O, HCl O + NH3 O - 9. Explain kinetic resolution ⇒ When you synthesize amino acids you’ll get a mixture of D and L – enantiomers have identical physical properties making it challenging to separate them – in kinetic resolution you can take advantage of the fact that certain enzymes (which are also chiral) will catalyze L faster than D (hence kinetic) in particular reactions – this alteration on the L amino acid makes it have different physical properties than the D and therefore can be separated by physical means such as chromatography or distillation 10. Draw the met-ile-tyr-asn-his at pH = 7 H N + H3N O N O NH NH NH NH2 O O O - O 11. Provide 2 ways the following peptide can be synthesized: p. 1077-1080 ala-gly-ser 12. Distinguish between primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary structures of peptides and proteins. primary ⇒ the sequence of the amino acids and the location of the disulfide bridges secondary ⇒ regular conformations assumed by segments of the protein’s backbone when it folds (in order to maximize H-bonds in the backbone) tertiary ⇒ the 3D structure of the entire protein quaternary ⇒ if a protein has more than one polypeptide chain (aka subunit) the quaternary structure is the way the individual subunits arrange themselves with respect to one another 13. Descibe denaturation and give examples of possible causes for denaturation. denaturation is destroying the highly organized tertiary structure of a protein – this may be caused by 1) changing pH 2) chemical reagents (ex: ox agent) 3) change the solvent or 4) heat or agitation 14. Show the cleavage sites on the following peptide if introduced to each of the following reagents: a. Carboxypeptidase A ⇒ ala-gly-phe-met-ser-lys-tyr-asn-glu-arg-pro-met-leu-his b. Edman’s ⇒ ala-gly-phe-met-ser-lys-tyr-asn-glu-arg-pro-met-leu-his c. Cyanogen bromide ⇒ ala-gly-phe-met-ser-lys-tyr-asn-glu-arg-pro-met-leu-his d. Trypsin ⇒ ala-gly-phe-met-ser-lys-tyr-asn-glu-arg-pro-met-leu-his e. Chymotrypsin ⇒ ala-gly-phe-met-ser-lys-tyr-asn-glu-arg-pro-met-leu-his