* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Part 3: Genetic Predictions Practice
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Inbreeding avoidance wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genome-wide association study wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Human leukocyte antigen wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
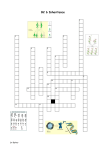
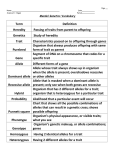
Name: ______________________________________________ Teacher: Rozema Hour: ____________ Unit 6-Heredity Unit Quiz #2 Review & Practice Part 1: Fill In The Blank Summary All individuals inherit ___________ alleles per _____________________________. One gene comes from our ______________________________ (from her egg cell), and one gene comes from our _______________________________ (from his sperm cell). When we inherit alleles, we can inherit… o Two of the _____________________ variations. This is called __________________________________. o Two ______________________ variations. This is called ___________________________________. There are 2 types of allele variations we can inherit: ___________________________________ and _____________________________________ ____________________________________ traits always show up. ____________________________________ traits only show up when ____________ are inherited together. We can use something called a _________________ chart to show the genotypes of parents and their offspring. In a PCR Chart, _______________________________________________ represents an individual having 2 of the same alleles…. While _________________________________________________ represents an individual having 2 different alleles. We can also use a ___________________________________ chart to show how individuals in a family are related to one another, and to make genetic _______________________________________________. When we make genetic _____________________________________________ we need to know the parents’ __________________________________ (or which variations they have for the trait). Genetic Predictions can show us…. o The different types of __________________________________________________________________ they can produce. o The ________________________________________________________ of producing different types of offspring. Part 2: Crossword Puzzle Practice -_- The school blocked my access to my crossword puzzle making website. So….. here it is lol… 1. A thick line in a PCR chart represents inheriting 2 of the __________ alleles inherited. Answer: 2. Which shape represents females in a pedigree chart? Answer: 3. We get one allele from our mother’s _________ cell. Answer: 4. If a person inherits 2 Dominant alleles for a trait, What will the person look like? Answer: 5. We get one allele from our father’s _________ cell. Answer: 6. All individuals inherit 2 of what per gene? Answer: 7. Having 2 different allele variations for a trait. Answer: 8. Which types of alleles always show up? Answer: 9. How many recessive alleles need to be inherited together for it to show up? Answer: 10. If a person inherits 1 Dominant and 1 Recessive allele for a trait, What will the person look like? Answer: 11. If a person inherits 2 Recessive alleles for a trait, What will the person look like? Answer: 12. Having 2 of the same allele variations for a trait. Answer: 13. Which types of alleles only show up when 2 are inherited? Answer: 14. Thin lines in a PCR chart represent inheriting 2 _____________ alleles inherited. Answer: 15. Which shape represents males in a pedigree chart? Answer: Part 3: Genetic Predictions Practice The following is a PCR Chart for 2 parents and their offspring: F1 M1 O1 O2 O3 O4 O5 O6 O7 O8 You are also told that the mother is Homozygous Recessive for the trait. 1. Using Black for the Dominant Trait, and White for the Recessive Trait, draw out a picture to represent the genotypes of the parents: 2. What variations can the mom pass on to her offspring in her eggs? 3. What variations can the dad pass on to his offspring in his sperm? 4. Set Up & Complete the following chart to show the possible offspring these 2 parents could produce: 5. List /Draw out all of the possible offspring these 2 parents could produce: 6. List out the percent chance of these 2 parents having each type of offspring: 7. Which trait would their kids look like? How do you know this? 8. Looking at the PCR Chart you see that they have kids either with a Solid Black Line, or 2 Thin Lines for their genotypes. Does this make sense? Why or Why not? 9. Which types of allele variations must the children with the Solid Black Line have inherited? Part 4: Genotype Phenotype Practice Normal Liver Diseased Liver DNA Sequence A-T-C-C-C-G-A-T-A-T-A-G A-T-C-G-C-G-A-T-A-T-A-G Amino Acid Chain Met-Val-Thr-Glu Met-Pro-Thr-Glu 10. Use what you know about DNA, Nitrogenous Bases, and Proteins, to explain how a person’s genotype could cause their body to develop the phenotype of a Diseased Liver instead of a Normal Liver: Part 5: Pedigree Prediction Practice 2 parents decide that they want to have kids, but they are curious what the chances are of them passing on a family disease. The disease happens to be a recessive trait. The mom is a carrier for the disease (meaning she has one allele that is recessive), and the dad does not have the trait at all. Again in answering any of the questions, use Black to represent the Dominant variation, and White to represent the Recessive variation. 11. What would have to be the genotype of a person with the disease? 12. What must be the genotype of the mom? How do you know this? 13. What must be the genotype of the dad? How do you know this? 14. Draw / Set Up a Chart to make a prediction about the types of offspring this couple could produce: 15. List out the different GENOTYPES (and the PERCENT CHANCE OF EACH) the parents could produce in their offspring: 16. List out the different PHENOTYPES (and the PERCENT CHANCE OF EACH) the parents could produce in their offspring: 17. Draw a Pedigree now to show the parents (their genotypes), and the possible offspring they could produce: