* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Causes of the Civil War
Missouri secession wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Missouri in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Wilson's Creek wikipedia , lookup
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
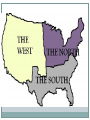
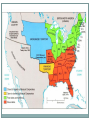
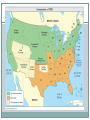
Causes of the Civil War Bellringer 66% of white southerners did NOT own slaves before the Civil War. Since this is the case, what was the war actually fought over? What are wars usually fought over? Learning Objectives SS.912.A.2.1: Review causes and consequences of the Civil War. Students will… Identify and explain the main forces that led to the Civil War. Distinguish the connections between events and ideas that led to this conflict. Justify their opinion on which cause had the greatest effect on initiating the war. Sectionalism Each region began to evolve along different paths. South – emphasis on slavery, cotton Northwest – small, independent farming; “bread basket” of country Northeast – manufacturing, factories Sectionalism People began feeling loyalty towards their regions over their nations. North wanted more active federal government that would promote industry South wanted very passive government because they wanted to maintain the status quo Slavery Abolitionists – reformers who wanted to get rid of slavery Frederick Douglass Sojourner Truth Harriet Tubman Uncle Tom’s Cabin – Harriet Beecher Stowe Slaves seen as inferior humans Afraid of what would happen if they were all freed (chaos, violence, decrease in status of whites) Westward Expansion How could they determine whether new territories would allow slavery or not? Both sides were afraid of being outnumbered in Congress Breakdown of Compromise Missouri Compromise, 1820 Free states = slave states, Missouri upset the balance Missouri became a slave state, Maine became a free state Established a line – all slavery above Missouri was banned, but below it was allowed Breakdown of Compromise Compromise of 1850 California wanted to be a free state Land gained from the Mexican-American War was a new problem So…California was admitted as a free state And…other territories were given “popular sovereignty” Harsher fugitive slave laws – free states had to return found slaves to their owners in the south Breakdown of Compromise Kansas-Nebraska Act, 1854 Proposed by Stephen Douglas, author of Compromise of 1820 Divided Nebraska territory into Nebraska and Kansas Gave the two new states popular sovereignty Resulted in the creation of the Republican party – Northerners were outraged that slavery could now be allowed in what had been free territory Breakdown of Compromise Bleeding Kansas, 1855-56 Kansas divided by Kansas-Nebraska Act Two rival governments formed Federal government forced to send troops in to quell violence Breakdown of Compromise Dred Scott Decision, 1857 Dred Scott, a slave from Missouri, lived in a free state with his owners for years then they all moved back In Missouri, he sued for his freedom Supreme Court decided as an African American, he wasn’t a citizen of the US AND ruled that the north had no right to prohibit slavery --- slaves were possessions and nothing more In response, Stephen Douglas published the Freeport Doctrine – claimed residents of states could still vote to ban slavery Breakdown of Compromise John Brown’s Raid, 1859 John Brown – white Northern abolitionist Tried to agitate slaves in South to revolt Captured federal arsenal in Harpers Ferry, Virginia Very few rebels participated – NO slaves Defeated and hung Instilled FEAR in Southerners States’ Rights Southerners supported more states’ rights John C. Calhoun claimed states could even cancel federal laws like taxes and tariffs This would also apply to leaving the Union altogether Northerners instead believed secession was illegal Election of Lincoln, 1860 No Southern states voted for Lincoln Immediately, S Carolina announced secession and was followed by 6 other states Southern states became Confederate States of America and elected Jefferson Davis as president Lincoln was determined to preserve the Union Shots fired at Fort Sumter initiated war Exit Slip 4 I can make in-depth inferences concerning the causes of the Civil War. 3 I can evaluate and assess the causes of the Civil War. 2 I can name the causes of the Civil War. 1 With help, I know some of 2 and 3 0 Even with help, I am unable to understand. 1. Rate yourself on the scale. 2. What would you claim is the most influential cause of the Civil War? Justify your answer. Bellringer Take out your textbook and turn to pg 101. Read the passages and answer the questions. When finished, complete your mind map from last class. Learning Objectives Students will… Compare and contrast the advantages and disadvantages of the North and the South. Analyze the effectiveness and consequences of the Emancipation Proclamation. Military Strategies Anaconda Plan North “strangle” the South’s economy with a naval blockade Seize control of the Mississippi River South hoped that Northern citizens would lose interest in the war and to get foreign support Instead… Lincoln suspended habeus corpus (no imprisonment without charge) and issued paper money conscription EOC Practice The excerpt below is from a letter by General Winfield Scott written in 1861 about the Anaconda Plan. “So as to envelope the insurgent States and bring them to terms, with less bloodshed than by any other plan.” What was the main objective of the plan described in General Scott’s letter? a) To attack and bring under control a few key Southern cities b) To disrupt Southern supply lines by controlling the railroad junctions in the South c) To sign treaties with Britain and France to prevent them from assisting the South d) To suffocate the South by controlling the Mississippi River and the Southern ports The excerpt below is from a letter by General Winfield Scott written in 1861 about the Anaconda Plan. “So as to envelope the insurgent States and bring them to terms, with less bloodshed than by any other plan.” What was the main objective of the plan described in General Scott’s letter? a) To attack and bring under control a few key Southern cities b) To disrupt Southern supply lines by controlling the railroad junctions in the South c) To sign treaties with Britain and France to prevent them from assisting the South d) To suffocate the South by controlling the Mississippi River and the Southern ports Major Battles Battle of Antietam – bloodiest day of the Civil War Emancipation Proclamation, Sept. 22, 1862 Why? Lincoln feared the South getting foreign aid Pressured by abolitionists to use war to end slavery But…still worried that ending slavery would alienate border states Emancipation Proclamation Textbook, pg 116 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pM3HS3rr-w0 Emancipation Proclamation Freed slaves in Confederacy…but not in the Union Officially made the war about slavery Turning Point, 1863 Gettysburg – Gettysburg Address 50,000 troops injured or killed Forced Confederates under General Lee to retreat The next day – Battle of Vicksburg Union General Ulysses S. Grant won over this city Gave Union control of the Mississippi River Valley Sherman’s March to the Sea General Grant wanted to destroy the Confederate army AND its base of support Sends General Sherman on a march from W Georgia to the coast Looted and burned farms, tore up railroad tracks Burned Atlanta to the ground Exit Slip Rate yourself on the scale 0-4. Burning questions Predict: Will the Emancipation Proclamation actually free the slaves? Bellringer 9/9 EOC practice pg 143 gold textbook Answer #s 1-4 on index card Final Days By 1865, Confederates very weak Gen. Grant takes Richmond, Confederate capital Apr. 9, 1865 – General Lee surrenders at Appomattox Courthouse One week later, Lincoln assassinated Consequences of the Civil War Ended slavery Re-affirmed existence of Union Strengthened powers of federal government 600,000 lives lost… Now…how do we recover? Florida in the Civil War Seceded from the Union, 1861 Long coastline made it easy to smuggle goods past the Union naval blockade into Confederate lands Central Florida used to grow food and keep cattle for Confederate troops What were the major consequences of the Civil War? a) The end of slavery and a strengthening of the power of the federal government b) Recognition of the rights of states to leave the Union and to nullify federal laws c) An end to racial discrimination and establishment of social equality throughout the nation d) The abolition of slavery in all Northern states and in all federal territories north of 36”30 N