* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cellular Transport – Active Transport Cells Review Questions
Survey
Document related concepts
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
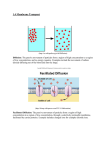
Cellular Transport – Active Transport Cells Review Questions Answer the following questions: 1. What is the function of the lysosomes in the cell? _____________________________________________________________________________________ 2. What is diffusion? _____________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Name 2 differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 4. What is osmosis? _____________________________________________________________________________________ 5. What is the function of the cell membrane? _____________________________________________________________________________________ Active Transport • Sometimes cells must move material against a concentration gradient – from *_________________________________* (It’s sort of like pushing your bike up a hill! – you need ____________________ to get that bike to the top) Active _________________________________________ Smaller molecules and ions carried across the membrane by ___________________ that act like ___________________________________________________ Examples: _________________________________________________________ Sodium-Potassium Pump __________________________________ are maintained at a ___________________________________ inside the cell, and ______________________ are maintained at ________________________________________________ inside the cell _________________________________ by protein molecules of the sodium and potassium ions is central to ______________________________________________________________________ Types of Active Transport: Endocytosis __________________________________________ must be transported across the membrane _____________________________ process of taking materials into the cell by means of “______________________” or ____________________________, of the cell membrane The pocket that forms from the membrane breaks loose and forms a ____________________________ What is the function of the vacuole in cells? ____________________________________________________________________________________ Two examples of endocytosis: ______________________________ “_________________________________;” extension of cytoplasm surround particle and package it within a food vacuole ( LARGE MOLECULES!!!) ______________________________ when cells take up liquid from surrounding environment. ----Tiny pockets form along membrane, fill with the liquid, and pinch off to form vacuoles within the cell Types of Active Transport: Exocytosis When cells ____________________ a large amount of material from the cell * Membrane of the vacuole ___________________________________________, forcing the contents ________________ of the cell* Complete the Chart Below Using Your Knowledge (And the Notes) about Endocytosis vs. Exocytosis Endocytosis Exocytosis 1. 1. 2. 2. 3. Overview 1. The cell membrane ______________________ what enters and exits the cell. The cell wall provides __________________________________________________________. 2. Particles move from an area of __________________________________________________ to an area of _________________________________________________. This process is called __________________________. 3. _________________________ is the diffusion of water through the __________________________________________________________________________ 4. The cell membrane is _________________________________________ and is made out of _____________________________________, that is where it gets one of its names: “__________________________________________________________________” 5. _______________________________________ – extensions of the cell membrane surround a particle and package it within a __________________________________ 6. _______________________________ – tiny pockets form along cell membrane, __________________________________________, and pinch off to form vacuoles inside the cell 7. ______________________________________ requires energy (______________) but diffusion does not require energy (_____________________________)