* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 1
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
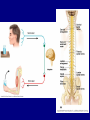
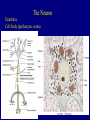
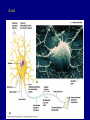
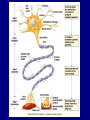
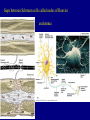
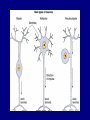
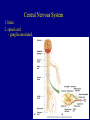
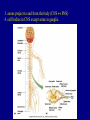
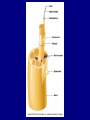
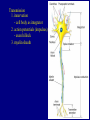
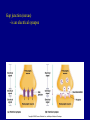
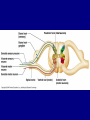
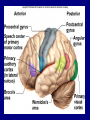
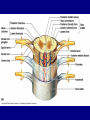
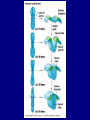
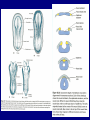
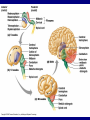
The Neuron Dendrites Cell body (perikaryon, soma) Axon Support cells (neuroglia) - more abundant than neurons - more mitotic capability Axon hillock Gaps between Schwann cells called nodes of Ranvier axolemma Myelinated axons: sheath of Schwann and myelin sheath one Schwann cell myelinates a single axon multiple Schwann cells needed to cover entire length of an axon Oligodendrocytes myelinate CNS axons (if myelinated) Central Nervous System 1. brain 2. spinal cord - ganglia associated 3. axons project to and from the body (CNS PNS) 4. cell bodies in CNS except some in ganglia Transmission 1. innervation - cell body as integrator 2. action potentials (impulses) - axon hillock 3. myelin sheath Synapses - presynaptic terminal - postsynaptic terminal - neurotransmitters - ligand-gated ions channels on postsynaptic membrane Gap junction (nexus) - is an electrical synapse Nervous System Organization of neurons 1. circuits for stimulus-response 2. exchange of information Neuron signaling 1. afferent vs. efferent 2. interneurons 3. circuits QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Anencephaly Anencephaly QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Spina bifida occulta with meningocoele QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Spina bifida with failure of neuropore closure QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Cortical dysplasia QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Cortical dysplasia QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture.