* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CH 460 Dr. Muccio What are the 4 levels of protein structure and
Survey
Document related concepts
Structural alignment wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Implicit solvation wikipedia , lookup
Bimolecular fluorescence complementation wikipedia , lookup
Protein domain wikipedia , lookup
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein folding wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Protein mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
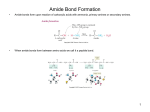
CH 460 Dr. Muccio What are the 4 levels of protein structure and describe each. Do proteins with similar structures usually have similar functions? Primary - amino acid sequence Secondary – helices, sheets, turns, loops Tertiary – 3d folding Quaternary – organization of 3d subunits Yes usually (not always), similar structure and similar function correlate _____ reactions lead to ____ bond formation, or peptide bonds. Draw an arrow to the peptide bond in the figure below. Aldol; covalent Condensation; amide Redox; amide Condensation; covalent None Peptides are named from their ____ end to their ____ end. So in the peptide “His-SerGln” which is on the amino end? The carboxy? Amino to carboxy, His, Gln What are the four types of secondary structure? What are they stabilized by? Can you draw them? Alpha helix – h-bonds in the same chain, few steric interaction Beta sheets - h-bonds between neighboring beta-strands, few steric interaction Beta turn – ONE h-bond, few steric interactions Loop/random – no h-bonds, few steric interactions When proteins are unfolded, they _____ to their native state which is ______ energy Do not return; high Return; high Do not return; low Return; low What are the forces that favor the native state? Hydrophobic forces – nonpolar amino acids will point towards the interior of proteins with fewer hydrophilic ones pointing out towards water Van der waals – due to the tight packing H-bonds – form h-bonds in the interior of proteins CH 460 Dr. Muccio